| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Chloride is important in acid–base balance in the extracellular space and has other functions, such as in the stomach, where it combines with hydrogen ions in the stomach lumen to form hydrochloric acid, aiding digestion. Its close association with Na + in the extracellular environment makes it the dominant anion of this compartment, and its regulation closely mirrors that of Na + .
The parathyroid glands monitor and respond to circulating levels of Ca ++ in the blood. When levels drop too low, PTH is released to stimulate the DCT to reabsorb Ca ++ from the forming urine. When levels are adequate or high, less PTH is released and more Ca ++ remains in the forming urine to be lost. Phosphate levels move in the opposite direction. When Ca ++ levels are low, PTH inhibits reabsorption of so that its blood level drops, allowing Ca ++ levels to rise. PTH also stimulates the renal conversion of calcidiol into calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D. Calcitriol then stimulates the intestines to absorb more Ca ++ from the diet.
The acid–base homeostasis of the body is a function of chemical buffers and physiologic buffering provided by the lungs and kidneys. Buffers, especially proteins, , and ammonia have a very large capacity to absorb or release H + as needed to resist a change in pH. They can act within fractions of a second. The lungs can rid the body of excess acid very rapidly (seconds to minutes) through the conversion of HCO 3 – into CO 2 , which is then exhaled. It is rapid but has limited capacity in the face of a significant acid challenge. The kidneys can rid the body of both acid and base. The renal capacity is large but slow (minutes to hours). The cells of the PCT actively secrete H + into the forming urine as Na + is reabsorbed. The body rids itself of excess H + and raises blood pH. In the collecting ducts, the apical surfaces of intercalated cells have proton pumps that actively secrete H + into the luminal, forming urine to remove it from the body.
As hydrogen ions are pumped into the forming urine, it is buffered by bicarbonate (HCO 3 – ), H 2 PO 4 – (dihydrogen phosphate ion), or ammonia (forming NH 4 + , ammonium ion). Urine pH typically varies in a normal range from 4.5 to 8.0.
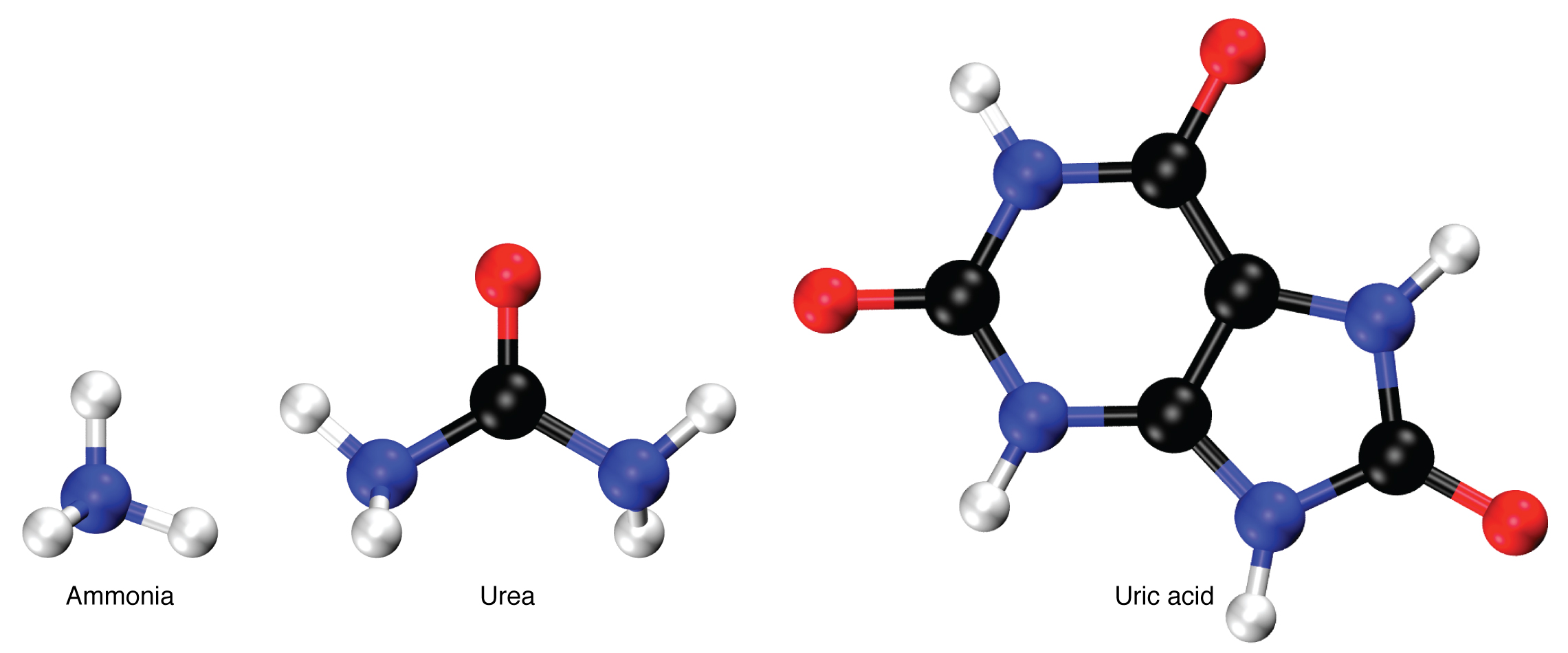
Nitrogen wastes are produced by the breakdown of proteins during normal metabolism. Proteins are broken down into amino acids, which in turn are deaminated by having their nitrogen groups removed. Deamination converts the amino (NH 2 ) groups into ammonia (NH 3 ), ammonium ion (NH 4 + ), urea, or uric acid ( [link] ). Ammonia is extremely toxic, so most of it is very rapidly converted into urea in the liver. Human urinary wastes typically contain primarily urea with small amounts of ammonium and very little uric acid.
Water-soluble drugs may be excreted in the urine and are influenced by one or all of the following processes: glomerular filtration, tubular secretion, or tubular reabsorption. Drugs that are structurally small can be filtered by the glomerulus with the filtrate. Large drug molecules such as heparin or those that are bound to plasma proteins cannot be filtered and are not readily eliminated. Some drugs can be eliminated by carrier proteins that enable secretion of the drug into the tubule lumen. There are specific carriers that eliminate basic (such as dopamine or histamine) or acidic drugs (such as penicillin or indomethacin). As is the case with other substances, drugs may be both filtered and reabsorbed passively along a concentration gradient.
The major hormones regulating body fluids are ADH, aldosterone and ANH. Progesterone is similar in structure to aldosterone and can bind to and weakly stimulate aldosterone receptors, providing a similar but diminished response. Blood pressure is a reflection of blood volume and is monitored by baroreceptors in the aortic arch and carotid sinuses. When blood pressure increases, more action potentials are sent to the central nervous system, resulting in greater vasodilation, greater GFR, and more water lost in the urine. ANH is released by the cardiomyocytes when blood pressure increases, causing Na + and water loss. ADH at high levels causes vasoconstriction in addition to its action on the collecting ducts to recover more water. Diuretics increase urine volume. Mechanisms for controlling Na + concentration in the blood include the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system and ADH. When Na + is retained, K + is excreted; when Na + is lost, K + is retained. When circulating Ca ++ decreases, PTH stimulates the reabsorption of Ca ++ and inhibits reabsorption of . pH is regulated through buffers, expiration of CO 2 , and excretion of acid or base by the kidneys. The breakdown of amino acids produces ammonia. Most ammonia is converted into less-toxic urea in the liver and excreted in the urine. Regulation of drugs is by glomerular filtration, tubular secretion, and tubular reabsorption.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?