| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Bào tử sinh dục khi hình thành có dạng túi gọi là nang (ascus) và túi này chứa những bào tử gọi là bào tử nang (ascospores). Nang và bào tử nang là đặc trưng của nhóm Ascomycetes (Hình 1.14) .
Trong nhóm Basidiomycetes, 4 bào tử phát triển ở phần tận cùng của cấu trúc thể quả gọi là đãm (basidium) và bào tử được gọi là bào tử đãm (basidiospores) (Hình 1.15)
Nhóm Nấm bất toàn (Deuteromycetes=Deuteromycotina)) gồm những nấm cho đến nay chưa biết rõ kiểu sinh sản hữu tính của chúng.
***SORRY, THIS MEDIA TYPE IS NOT SUPPORTED.***
Hình 3.2.1 Các kiểu hình thành tiếp hợp tử ở Mucoraceae. a-f. Rhizopus.
g-h. Zygorhynchus, i. Absidia, j. Phycomyces (theo Talbot, 1995)
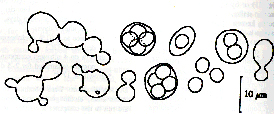
Hình 1.13. Bào tử nang ở Saccharomyces cerevisiae (theo Samson và
ctv. 1995)
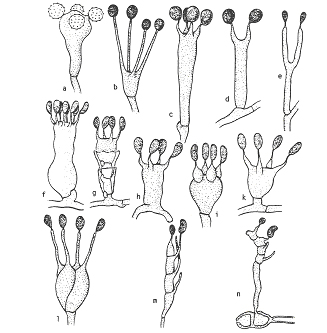
Hình 1.14. Các kiểu bào tử đảm. a. Astrea, b. Bovista, c. Agaricales,
d. Clavulina, e. Dacrymyces, f. Sistotrema, g. Repetobasidium, h. Xenasma,
i-n. bào tử đảm có vách, n. Puccinia. (theo Kreisel, 1995)
Nấm mốc có ảnh hưởng xấu đến cuộc sống con người một cách trực tiếp bằng cách làm hư hỏng, giảm phẩm chất lương thực, thực phẩm trước và sau thu hoạch, trongchế biến, bảo quản. Nấm mốc còn gây hư hại vật dụng, quần áo... hay gây bệnh cho người, động vật khác và cây trồng. Tuy nhiên, các qui trình chế biến thực phẩm có liên quan đến lên men đều cần đến sự có mặt của vi sinh vật trong đó có nấm mốc. Nấm mốc cũng giúp tổng hợp những loại kháng sinh (penicillin, griseofulvin), acit hữu cơ (acit oxalic, citric, gluconic...), vitamin (nhóm B, riboflavin), kích thích tố (gibberellin, auxin, cytokinin), một số enzim và các hoạt chất khác dùng trong công nghiệp thực phẩm và y, dược ... đã được sử dụng rộng rãi trên thế giới. Ngoài ra, nấm còn giử vai trò quan trọng trong việc phân giải chất hữu cơ trả lại độ mầu mỡ cho đất trồng.
Một số loài thuộc giống Rhizopus, Mucor, Candida gây bệnh trên người, Microsporum gây bệnh trên chó, Aspergillus fumigatus gây bệnh trên chim; Saprolegnia và Achlya gây bệnh nấm ký sinh trên cá. Những loài nấm gây bệnh trên cây trồng như Phytophthora, Fusarium, Cercospora.... đặc biệt nấm Aspergilus flavus và Aspergillus fumigatus phát triển trên ngũ cốc trong điều kiện thuận lợi sinh ra độc tố aflatoxin.
Bên cạnh tác động gây hại, một số loài nấm mốc rất hữu ích trong sản xuất và đời sống như nấm ăn, nấm dược phẩm (nấm linh chi, Penicillium notatum tổng hợp nên penicillin, Penicillium griseofulvum tổng hợp nên griseofulvin...), nấm Aspergillus niger tổng hợp các acit hữu cơ như acit citric, acit gluconic, nấm Gibberella fujikuroi tổng hợp kích thích tố gibberellin và một số loài nấm thuộc nhóm Phycomycetina hay Deuteromycetina có thể ký sinh trên côn trùng gây hại qua đó có thể dùng làm thiên địch diệt côn trùng. Ngoài ra, những loài nấm sống cộng sinh với thực vật như Nấm rễ (Mycorrhizae), giúp cho rễ cây hút được nhiều hơn lượng phân vô cơ khó tan và cung cấp cho nhu cầu phát triển của cây trồng.
Nấm còn là đối tượng nghiên cứu về di truyền học như nấm Neurospora crassa, nấm Physarum polycephalum dùng để tổng hợp ADN và những nghiên cứu khác.
Đầu tiên, nấm được sắp xếp theo tiến hóa như mô hình dưới đây: (Hình 1.15)
Dayal (1975) liệt kê 7 đặc tính để phân loại nấm mốc như sau:
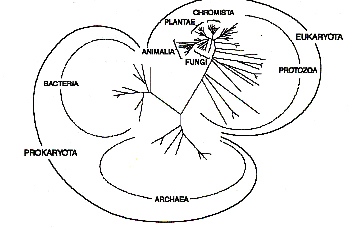
Hình 1.15 Cây di truyền phát sinh ngành cho thấy nấm mốc có mối liên hệ gần với
thực vật (PLANTAE) và động vật (ANIMALIA) (theo Hawkswort và
ctv., 1995)
Theo Gwynne-Vaughan và Barnes (1937) chia nấm thành 3 lớp chính: Phycomycetes, Ascomycetes và Basidiomycetes dựa trên khuẩn ty có vách ngăn ngang hay không và đặc điểm của bào tử. Theo Stevenson (1970) đã phân loại nấm trong ngành Mycota gồm 6 lớp: Chytridiomycetes, Oomycetes, Zygomycetes, Ascomycetes, Basidiomycetes, và Deuteromycetes. Gần đây, Kurashi (1985) nhấn mạnh đến tầm quan trọng của hệ thống ubiquinon trong phân loại nấm mốc cũng như ứng dụng kỹ thuật sinh học phân tử để khảo sát đa dạng di truyền và qua mối liên hệ di truyền phân loại lại cho chính xác hơn.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Giáo trình môn nấm học' conversation and receive update notifications?