| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
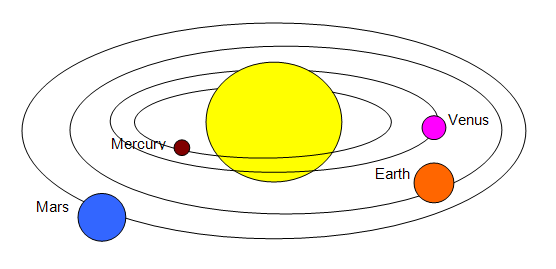
The following diagram shows the inner planets of our solar system:
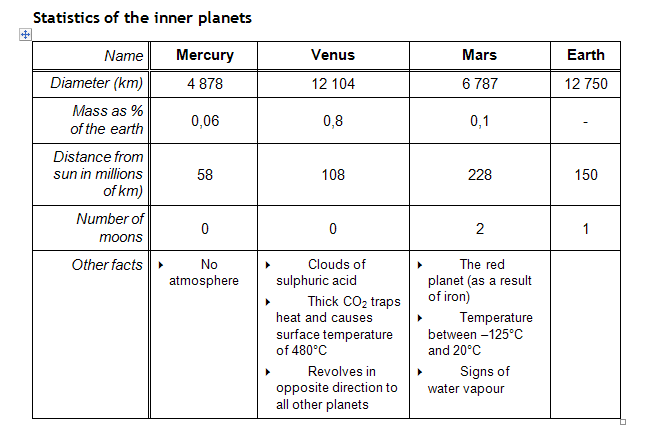
Statistics of
Activity: INTERPRETATION
2. Which planet is closest to the sun?
3. Which planet is furthest from the sun in the diagram? ………………………………………..
5. Which planet is called the earth’s twin because it looks the same from space?
6. Which planet of this group has features that show the greatest resemble to those of the earth?
Activity: Draw the orbits
[LU 2.1]
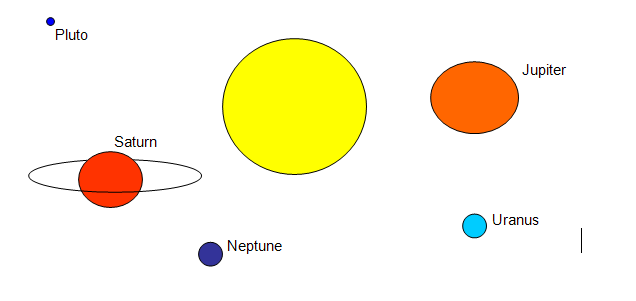
The following diagram shows the outer planets of our solar system.
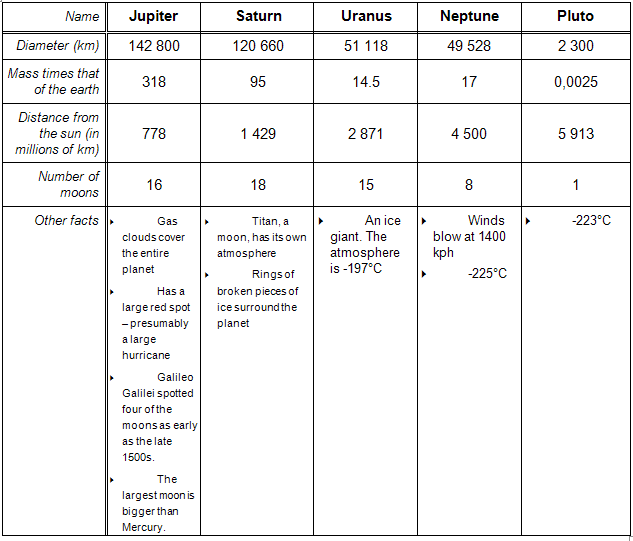
Statistics of the outer planets
Activity: QUESTIONS
Which planet …
1. has a red spot?
2. has rings of ice?
3. has the strongest winds?.
4. has the largest mass?
5. has the most moons?
6. is the coldest?
7. has the largest diameter?
8. has the highest temperature?
9. has a moon with an atmosphere? .
10. has a moon larger than another planet?
Assessment of QUESTIONS ON PLANETS: Did you answer the questions correctly? [ LO 2.3]
Activity: CALCULATING DISTANCES (interpretation task)
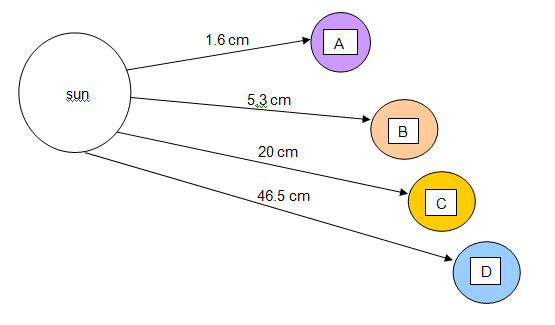
Assignment: INTERPRETATION TASK
1. Study the above values and suggested distances from the sun.
1 cm = 1 Astronomical unit
Identify the planets:
A __________________
B ____________________
C _______________
D _________________
2. Arrange the planets from the largest to the smallest.
3. What planet is 5 times further than the earth from the sun?
4. What planet is 30 times further than the earth from the sun?
5. The gravity of Mars is 0,39 that of the earth. If you weigh 100 kg on earth, you would weigh 100 x 0,39 kg, i.e. 39 kg, on Mars.
How much do you weigh on earth? ……………………………
Calculate how much you would weigh on the following planets and complete the table:
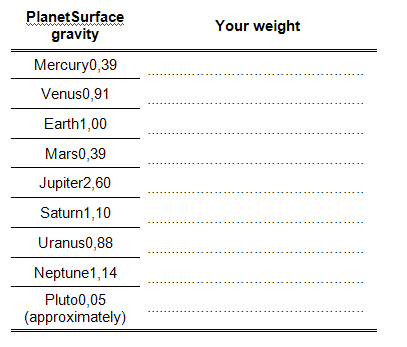
6. On which planet would you:
(a) weigh the least?
(b) weigh the most?
Assessment of INTERPRETATION TASK:
Did you do the conversions correctly? Could you categorise the information?
[LO 2.2; LO 2.4]
Activity : GROUP WORK
CONSTRUCT A SOLAR SYSTEM
Assessment of CONSTRUCTION PROJECT:
Did you a) plan how you would obtain information, b) collect information and c) communicate information and findings?
[LO 1.1; LO 1.2; LO 1.3; LO 3.1]
LO 1: Scientific investigations:
The learner will be able to act confidently on curiosity about natural phenomena, and to investigate relationships and solve problems in scientific, technological and environmental contexts.
This is evident when the learner:
LO 2: Constructing Science Knowledge:
The learner will know and be able to interpret and apply scientific, technological and environmental knowledge.
This is evident when the learner:
2.4 applies knowledge.
LO 3: Science, Society and the Environment
The learner will be able to demonstrate an understanding of the interrelationships between science and technology, society and the environment.
This is evident when the learner:
3.1 understands science as a human endeavour.
ACTIVITY: INTERPRETATION
1. 9
2. Mercury
3. Neptune
4. elliptical
5. Venus
6. Mars
ACTIVITY: QUESTIONS – Which planet….
1. Jupiter
2. Saturn
3. Neptune
4. Jupiter
5. Saturn
6. Neptune
7. Jupiter
8. Mercury
9. Saturn's Titan
10. Ganymede, of Jupiter, is the largest one in our galaxy and is bigger than Mercury
ACTIVITY: CALCULATING DISTANCES (translation)
1. A = Mars ( 1,6 x 150 milj)B= JupiterC = UranusD= Pluto
2. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Earth, Venus, Mars, Mercury, and Pluto
3. Jupiter
4. Neptune
5. Each according to its own mass
6a) Pluto
6b) Jupiter

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural sciences grade 9' conversation and receive update notifications?