| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Introduction
What is a mechanism?
Activity 1
| LO 1.2 | ||||
Mechanisms and Motion
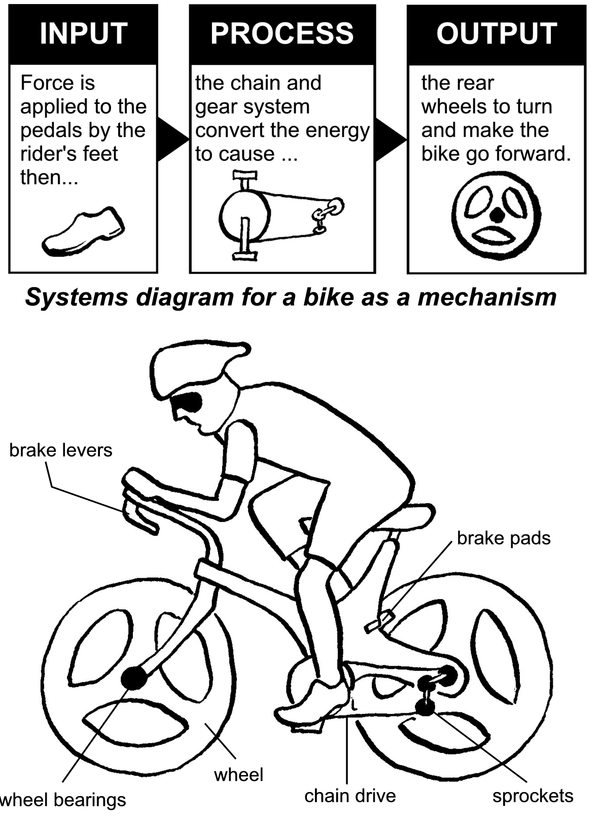
Activity 2
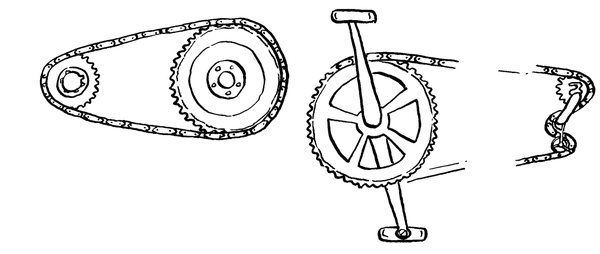
| LO 2.3 | ||||
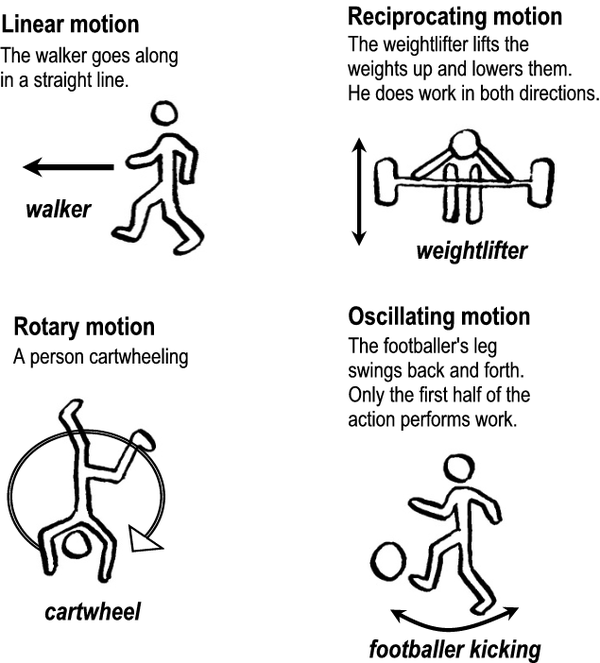
Activity 3
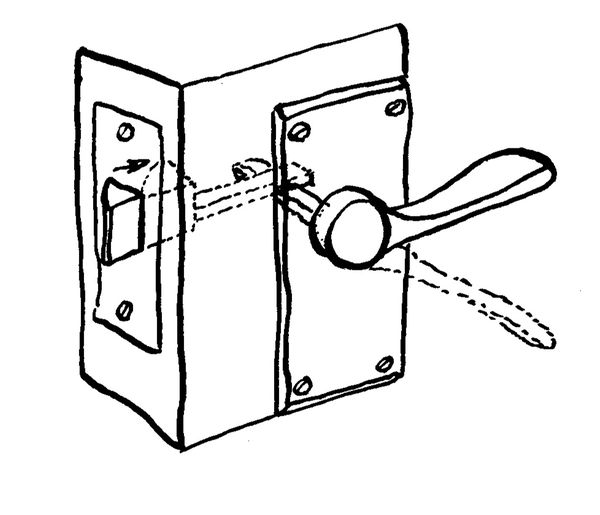
| LO 2.3 | ||||
Types of mechanisms
Mechanisms are used in machinery. There are five types of mechanism:
Activity 4
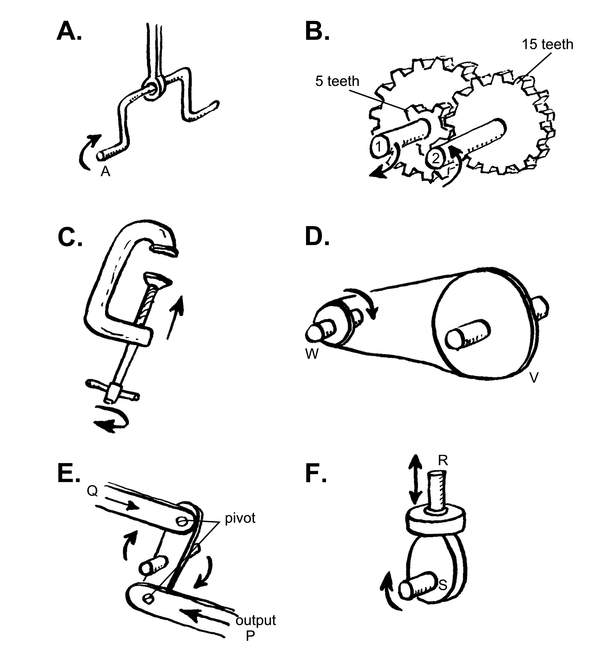
| LO 2.3 | ||||
| Learning outcomes(LOs) |
| LO 1 |
| TECHNOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND SKILLS The learner will be able to apply technological processes and skills ethically and responsibly using appropriate information and communication technology. |
| Assessment standards(ASs) |
| We know this when the learner: |
investigates:1.2 analyses existing products relevant to an identified problem, need or opportunity based on:
|
| LO 2 |
| TECHNOLOGICAL KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING The learner will be able to understand and apply relevant technological knowledge ethically and responsibly. |
| We know this when the learner: |
systems and control:2.3 demonstrates knowledge and understanding of interacting mechanical systems and sub-systems by practical analysis and represents them using system diagrams:
|
ACTIVITY 1
ACTIVITY 2
2.1 Greater forces can be transferred
2.2 Chains do not slip/slide
2.3 Chains can be unlinked to facilitate removal
ACTIVITY 3
ACTIVITY 4
B – Gears
C – Propeller/screw
D – Pulley
E – Linkage/linking
F – Cam

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Technology grade 9' conversation and receive update notifications?