| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
1. (b) quadrate number
2.
(a)
(b) No not quadrate of number
(c) No 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 4 5
3.
(b) 64; 125; 216; 343
(c) 64
(d) 64 000
(e) 274 625
(f) K4: + 64
K5: + 64 + 125 = 225
(g) 1 + 8 + 27 + 64 + 125 + 216 = 441
(h) all square number
1. Do you still remember?
In module 1 we learnt about square numbers and triangular numbers.
a) Can you explain to your partner what these patterns are like?
b) What is the synonym for square numbers?
2. Let us have a look at RECTANGULAR NUMBERS.
Did you know?
Each counting number bigger than 0 is a rectangular number. The Greeks used the term rectangular number for the product of two consecutive numbers only,
e.g. 42 = 6 x 7.
When we draw rectangular numbers, they will look like this:
| ___ | ___ | ___ | ___ | ___ | ___ | ___ | ___ | ___ | |||
| 6 = 1 × 6 | ___ | ___ | ___ | ||||||||
| 6 = 2 × 3 |
a) Now draw as many sketches as possible to represent the rectangular number 18.
b) Is 18 a square number? ______________________________ Why/why not?
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
c) Is 18 a triangular number? ___________________________ Why/why not?
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
3. Did you know?
a) We also have numbers to the power of three!! These numbers are also known as cubed numbers. Take a good look at the examples:
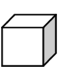
1 = 1 × 1 × 1
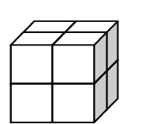
8 = 2 × 2 × 2
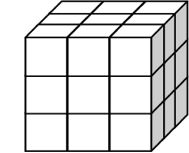
27 = 3 × 3 × 3
b) Predict what the following four cubed numbers will be (you may use your pocket calculator).
___________________________;
___________________________;
___________________________;
___________________________;
c) List any of the above numbers that may be a square number:______________
d) What will the 40th cubed number be? _______________________________
e) What is 653 (to the power of 3)? ___________________________________
f) Take a good look at the following. Can you complete the table?
| Cubed numbers | Sum of the cubed numbers |
| K1 | 1 |
| K2 | 1 + 8 = 9 |
| K3 | 1 + 8 + 27 = 36 |
| K4 | 1 + 8 + 27 + ........... = 100 |
| K5 | 1 + 8 + 27 + ........... + ........... = ......................... |
g) Can you predict what the sum of the first 6 cubed numbers will be?
_____________________________________________________________________
h) What do you notice about the numbers in the second column?
_____________________________________________________________________
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check with competence and confidence in solving problems.
Assessment Standard 1.3: We know this when the learner recognises, classifies and represents the following numbers in order to describe and compare them:
1.3.4: numbers in exponential form including squares of natural numbers to at least 12 2 , cubes of natural numbers to at least 5 3 , and their square and cube roots.
Assessment Standard 1.7: We know this when the learner estimates and calculates by selecting and using operations appropriate to solving problems that involve:
1.7.2: multiple operations with integers;
1.7.7: exponents.
Learning Outcome 2: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent patterns and relationships, as well as to solve problems using algebraic language and skills.
Assessment Standard 2.3: We know this when the learner represents and uses relationships between variables in order to determine input and/or output values in a variety of ways using:
2.3.1: verbal descriptions;
2.3.3: tables.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?