| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
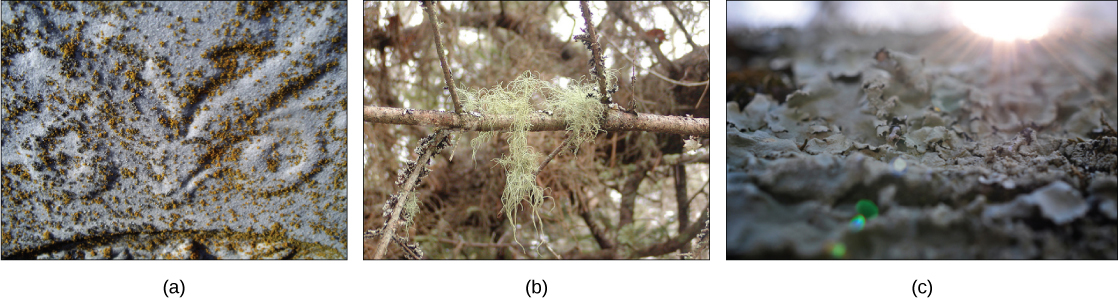
Lichens display a range of colors and textures ( [link] ) and can survive in the most unusual and hostile habitats. They cover rocks, gravestones, tree bark, and the ground in the tundra where plant roots cannot penetrate. Lichens can survive extended periods of drought, when they become completely desiccated, and then rapidly become active once water is available again.
Explore the world of lichens using this site from Oregon State University.
Lichens are not a single organism, but rather an example of a mutualism, in which a fungus (usually a member of the Ascomycota or Basidiomycota phyla) lives in close contact with a photosynthetic organism (a eukaryotic alga or a prokaryotic cyanobacterium) ( [link] ). Generally, neither the fungus nor the photosynthetic organism can survive alone outside of the symbiotic relationship. The body of a lichen, referred to as a thallus, is formed of hyphae wrapped around the photosynthetic partner. The photosynthetic organism provides carbon and energy in the form of carbohydrates. Some cyanobacteria fix nitrogen from the atmosphere, contributing nitrogenous compounds to the association. In return, the fungus supplies minerals and protection from dryness and excessive light by encasing the algae in its mycelium. The fungus also attaches the symbiotic organism to the substrate.
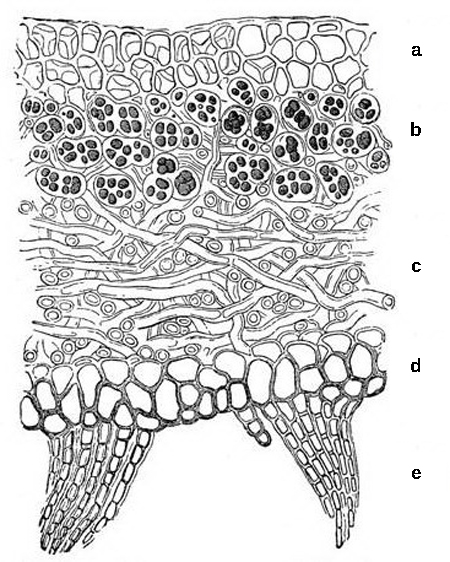
The thallus of lichens grows very slowly, expanding its diameter a few millimeters per year. Both the fungus and the alga participate in the formation of dispersal units for reproduction. Lichens produce soredia , clusters of algal cells surrounded by mycelia. Soredia are dispersed by wind and water and form new lichens.
Lichens are extremely sensitive to air pollution, especially to abnormal levels of nitrogen and sulfur. The U.S. Forest Service and National Park Service can monitor air quality by measuring the relative abundance and health of the lichen population in an area. Lichens fulfill many ecological roles. Caribou and reindeer eat lichens, and they provide cover for small invertebrates that hide in the mycelium. In the production of textiles, weavers used lichens to dye wool for many centuries until the advent of synthetic dyes.
Lichens are used to monitor the quality of air. Read more on this site from the United States Forest Service.
Animal dispersal is important for some fungi because an animal may carry spores considerable distances from the source. Fungal spores are rarely completely degraded in the gastrointestinal tract of an animal, and many are able to germinate when they are passed in the feces. Some dung fungi actually require passage through the digestive system of herbivores to complete their lifecycle. The black truffle—a prized gourmet delicacy—is the fruiting body of an underground mushroom. Almost all truffles are ectomycorrhizal, and are usually found in close association with trees. Animals eat truffles and disperse the spores. In Italy and France, truffle hunters use female pigs to sniff out truffles. Female pigs are attracted to truffles because the fungus releases a volatile compound closely related to a pheromone produced by male pigs.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bi 101 for lbcc ilearn campus' conversation and receive update notifications?