| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
There are now two DNA molecules. Each consists of an original nucleotide strand next to a new complementary strand. The two molecules are identical to each other.
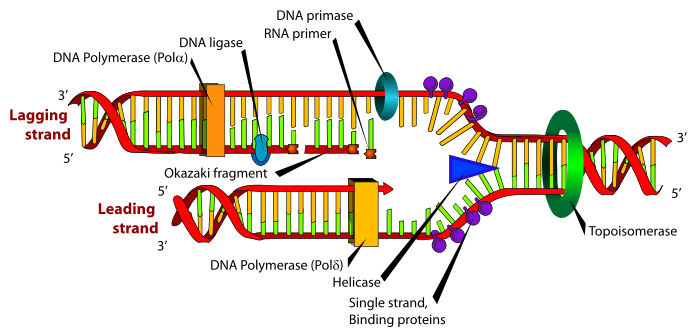
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/9f/DNA_replication.svg/691px-DNA_replication.svg.png
Genetic information likes a language. We use letters of the alphabet to make words and then join these words together to make sentences, paragraphs and books. In the case of DNA :
Let’s make some comparisons between English Language and Genetic Language:
| English Language FIXME: A LIST CAN NOT BE A TABLE ENTRY.We use 26 letters to make words. The words can be any length we need. We join words together to create sentences Each sentence starts with a capital letter.Each sentence ends with a fullstop .All the sentences combine to form a book . | Genetic Language FIXME: A LIST CAN NOT BE A TABLE ENTRY.DNA uses 4 molecules to make codons. The codons can only be 3 nucleotides long. The codons join together to form genes . The gene starts with codon AUG.The gene stops at a specific stop codon . All the genes combine to form the genome . |
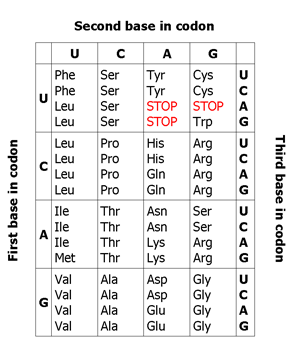
Along the gene (and DNA itself) the information for the amino acids that will make up the gene is stored in three-letter words called codons . Each codon specifies a particular amino acid. By "reading" this set of codons, the specific protein can be generated from this chunk of genetic code. The codons on DNA code for a specific amino acid . There are 20 amino acids commonly found in natural proteins .
Below is a “paragraph” of gene language:
CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG TGA CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG TGA CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG TGA CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG TGA CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG TGA CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG TGA CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG TGA CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG TGA CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG TGA CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG TGA CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG TGA CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG TGA CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG TGA CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG GAA GAG TGA CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG TGA CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG TGA CCG ACG TCC GAA GAG TGA CCG

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Genetics' conversation and receive update notifications?