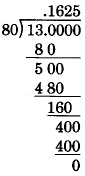This module is from Elementary Algebra by Denny Burzynski and Wade Ellis, Jr.
This chapter contains many examples of arithmetic techniques that are used directly or indirectly in algebra. Since the chapter is intended as a review, the problem-solving techniques are presented without being developed. Therefore, no work space is provided, nor does the chapter contain all of the pedagogical features of the text. As a review, this chapter can be assigned at the discretion of the instructor and can also be a valuable reference tool for the student.
Overview
- Decimal Fractions
- Adding and Subtracting Decimal Fractions
- Multiplying Decimal Fractions
- Dividing Decimal Fractions
- Converting Decimal Fractions to Fractions
- Converting Fractions to Decimal Fractions
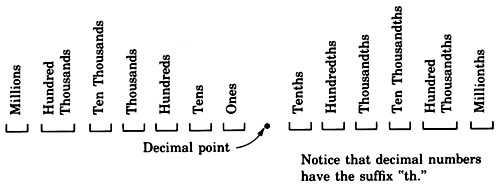
Decimal fractions
Fractions are one way we can represent parts of whole numbers. Decimal fractions are another way of representing parts of whole numbers.
Decimal fractions
A
decimal fraction is a fraction in which the denominator is a power of 10.
A decimal fraction uses a
decimal point to separate whole parts and fractional parts. Whole parts are written to the
left of the decimal point and fractional parts are written to the
right of the decimal point. Just as each digit in a whole number has a particular value, so do the digits in decimal positions.
Sample set a
The following numbers are decimal fractions.
Adding and subtracting decimal fractions
Adding/subtracting decimal fractions
To add or subtract decimal fractions,
- Align the numbers vertically so that the decimal points line up under each other and corresponding decimal positions are in the same column. Add zeros if necessary.
- Add or subtract the numbers as if they were whole numbers.
- Place a decimal point in the resulting sum or difference directly under the other decimal points.
Sample set b
Find each sum or difference.
Multiplying decimal fractions
Multiplying decimal fractions
To multiply decimals,
- Multiply tbe numbers as if they were whole numbers.
- Find the sum of the number of decimal places in the factors.
- The number of decimal places in the product is the sum found in step 2.
Sample set c
Find the following products.


Dividing decimal fractions
Dividing decimal fractions
To divide a decimal by a nonzero decimal,
- Convert the divisor to a whole number by moving the decimal point to the position immediately to the right of the divisor’s last digit.
- Move the decimal point of the dividend to the right the same number of digits it was moved in the divisor.
- Set the decimal point in the quotient by placing a decimal point directly above the decimal point in the dividend.
- Divide as usual.
Sample set d
Find the following quotients.


Check by multiplying
and
This will show that we have obtained the correct result.

Converting decimal fractions to fractions
We can convert a decimal fraction to a fraction by reading it and then writing the phrase we have just read. As we read the decimal fraction, we note the place value farthest to the right. We may have to reduce the fraction.
Sample set e
Convert each decimal fraction to a fraction.
Converting fractions to decimal fractions
Sample set f
Convert the following fractions to decimals. If the division is nonterminating, round to 2 decimal places.




This is a complex decimal. The “6” is in the hundredths position. The number
is read as “sixteen and one-fourth hundredths.”
Now, convert
to a decimal.
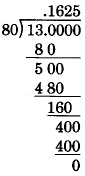
Exercises
For the following problems, perform each indicated operation.
For the following problems, convert each decimal fraction to a fraction.
For the following problems, convert each fraction to a decimal fraction. If the decimal form is nonterminating,round to 3 decimal places.