| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The absolute refractory period for cardiac contractile muscle lasts approximately 200 ms, and the relative refractory period lasts approximately 50 ms, for a total of 250 ms. This extended period is critical, since the heart muscle must contract to pump blood effectively and the contraction must follow the electrical events. Without extended refractory periods, premature contractions would occur in the heart and would not be compatible with life.
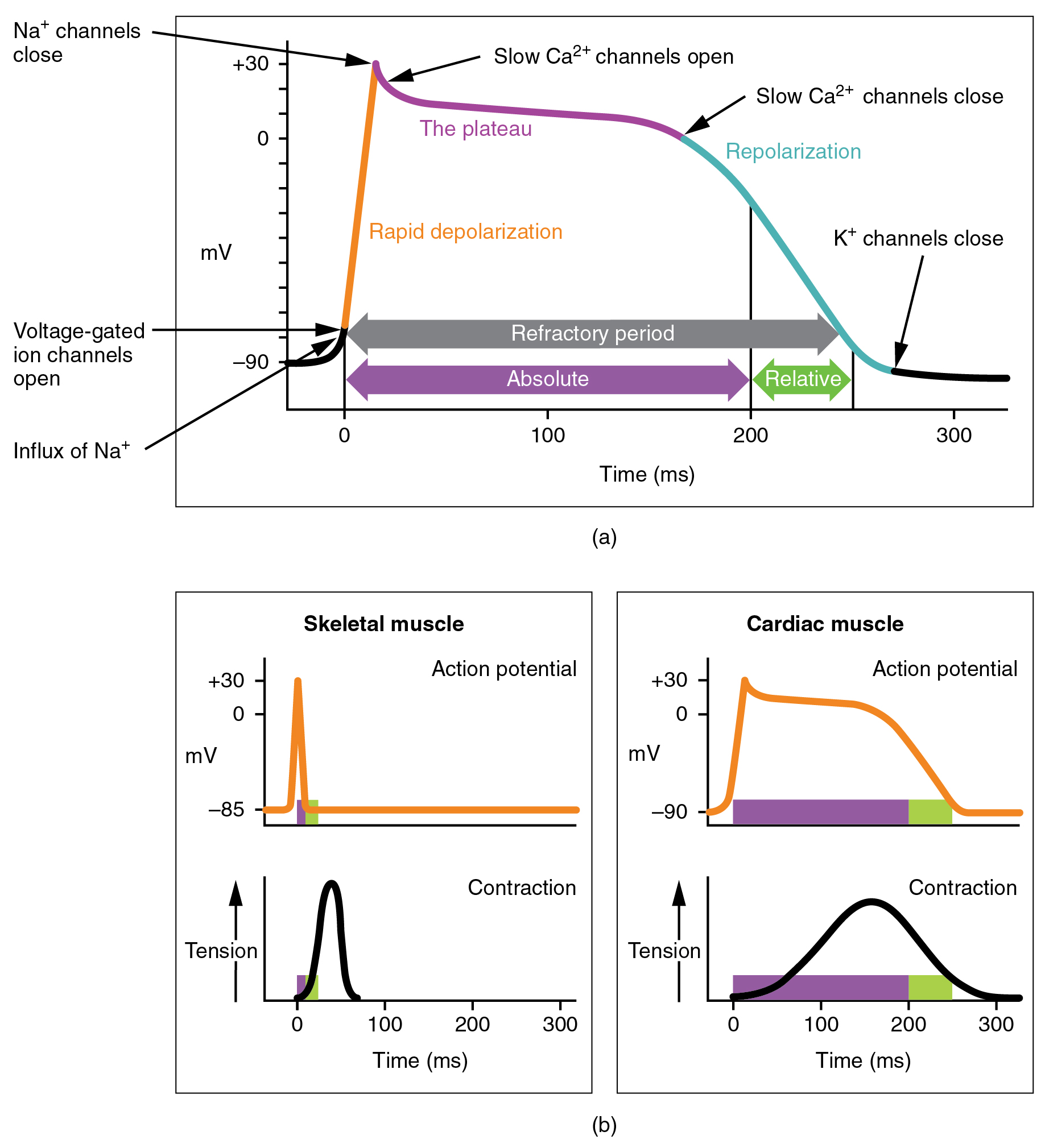
Calcium ions play two critical roles in the physiology of cardiac muscle. Their influx through slow calcium channels accounts for the prolonged plateau phase and absolute refractory period that enable cardiac muscle to function properly. Calcium ions also combine with the regulatory protein troponin in the troponin-tropomyosin complex; this complex removes the inhibition that prevents the heads of the myosin molecules from forming cross bridges with the active sites on actin that provide the power stroke of contraction. This mechanism is virtually identical to that of skeletal muscle. Approximately 20 percent of the calcium required for contraction is supplied by the influx of Ca 2+ during the plateau phase. The remaining Ca 2+ for contraction is released from storage in the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
The pattern of prepotential or spontaneous depolarization, followed by rapid depolarization and repolarization just described, are seen in the SA node and a few other conductive cells in the heart. Since the SA node is the pacemaker, it reaches threshold faster than any other component of the conduction system. It will initiate the impulses spreading to the other conducting cells. The SA node, without nervous or endocrine control, would initiate a heart impulse approximately 80–100 times per minute. Although each component of the conduction system is capable of generating its own impulse, the rate progressively slows as you proceed from the SA node to the Purkinje fibers. Without the SA node, the AV node would generate a heart rate of 40–60 beats per minute. If the AV node were blocked, the atrioventricular bundle would fire at a rate of approximately 30–40 impulses per minute. The bundle branches would have an inherent rate of 20–30 impulses per minute, and the Purkinje fibers would fire at 15–20 impulses per minute. While a few exceptionally trained aerobic athletes demonstrate resting heart rates in the range of 30–40 beats per minute (the lowest recorded figure is 28 beats per minute for Miguel Indurain, a cyclist), for most individuals, rates lower than 50 beats per minute would indicate a condition called bradycardia. Depending upon the specific individual, as rates fall much below this level, the heart would be unable to maintain adequate flow of blood to vital tissues, initially resulting in decreasing loss of function across the systems, unconsciousness, and ultimately death.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?