| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Dựa trên lý luận này, George Lemaitre người Bỉ và sau đó George Gamow cùng Alexandre Priedmann người Nga, bằng các phép tính có cơ sở vật lý đúng đắn, đã nêu ra học thuyết về sự hình thành của vũ trụ, gọi là thuyết Big Bang. Thuyết này cho rằng vũ trụ được sinh ra cách đây khoảng 15 tỷ năm từ một quả trứng cực nhỏ, có khối lượng (M), năng lượng (E) và nhiệt độ (T) cực lớn bởi một vụ nổ lớn gọi là Big Bang. Vụ nổ này tạo ra không gian - thời gian và toàn bộ Vũ trụ, theo quá trình dãn nở như sau:
Bảng 1.1. Tóm tắt lịch sử của Vũ trụ
| Thời gian | Nhiệt độT (K) | Thành phần của Vũ trụ | Đặc điểm của Vũ trụ |
| 10-43s | T1032K | Một chất điểm có M, E, T cực lớn | 1 siêu lực, r = 10-35m |
| 10-35s | 1027K | Chân không lượng tử, trường năng lượng đồng nhất | 2 lực: Điện hạt nhân (HN), hấp dẫn (HD) |
| 10-32s | 1025K | Dãn nở tạo không gian, ngưng kết | 3 lực: HN, điện từ (ĐT) và HD |
| 10-12s | 1015K | Nhiệt độ giảm, tạo hạt quarks | 3 lực: HN, ĐT và HD |
| 10-6s | 1013K | Tạo photon, điện tử, lepton | 4 lực: HN, ĐT, Từ trường yế và HD |
| 3phút | 106K | Tạo proton, neutron | P = uud, n = udd |
| 3.105năm | 104K | Tạo nhân H, He | He = 2p2n, hạt nhân H |
| 109 năm | 102K | Tạo khí H2, He, tinh vân và các thiên hà | Có khí H2, tinh vân |
| 1010năm | 10 K | Tạo mặt trời, hệ MT, tạo các nguyên tố nặng | Có thiên hà, các sao, hành tinh |
| 12.109n | 7 K | Tạo khí quyển, lục địa, núi | Tạo nguyên tố nặng, sao thứ cấp, núi |
| 14.109 n | 5 K | Tạo nước, đại dương, vi khuẩn, tảo, sinh vật | Có nước, đại dương, sinh vật |
| 15.109n | 3 K | Tạo động vật, khỉ, người | Sinh vật cao, khỉ, người |
Một tỷ năm sau vụ nổ Big Bang, Vũ trụ dãn nở làm nhiệt độ giảm đến 100K. Lúc này các nhân H, He kết hợp với điện tử tạo ra phân tử khí H2, He. Các khí này quây tụ thành từng đám trong thiên hà. Từ mỗi đám bụi này, do tác dụng của lực hấp dẫn, sẽ dần dần hình thành một hệ mặt trời.
Hệ mặt trời của ta thuộc thế hệ thứ 3, được sinh ra từ một đám mây bụi và khí có kích thước hàng ngàn tỷ kilômét.
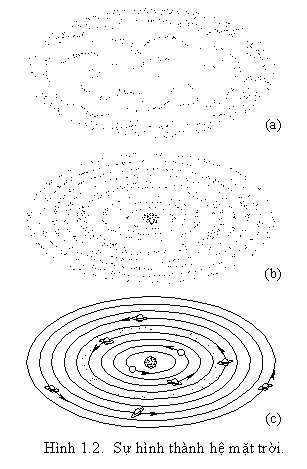
Dưới tác dụng của lực hấp dẫn, đám mây bắt đầu co lại, dẹt đi, và tâm của nó trở nên đặc và nóng dần, đến mức có thể khởi phát các phản ứng hạt nhân và trở thành mặt trời. Khí và bụi ít đặc hơn phía ngoài sẽ quay quanh mặt trời, kết thành các vành đai, ngưng tụ thành các hành tinh và tiểu hành tinh. Phần khí loãng quanh hành tinh cũng ngưng kết theo cách tương tự để tạo ra các vệ tinh quay quanh hành tinh.
Hệ mặt trời gồm có mặt trời và 9 hành tinh quay quanh nó, theo các quỹ đạo ellip gần tròn. Vòng trong có 4 hành tinh dạng rắn là sao Thủy, sao Kim, quả Đất, sao Hỏa, vòng ngoài có 5 hành tinh dạng khí là sao Mộc, sao Thổ, sao Thiên Vương, sao Hải Vương, sao Diêm Vương.
Giữa sao Hỏa và sao Mộc có một vành đai gồm các tiểu hành tinh với đường kính từ vài chục mét tới vài trăm kilômét.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Năng lượng mặt trời- lý thuyết và ứng dụng' conversation and receive update notifications?