| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
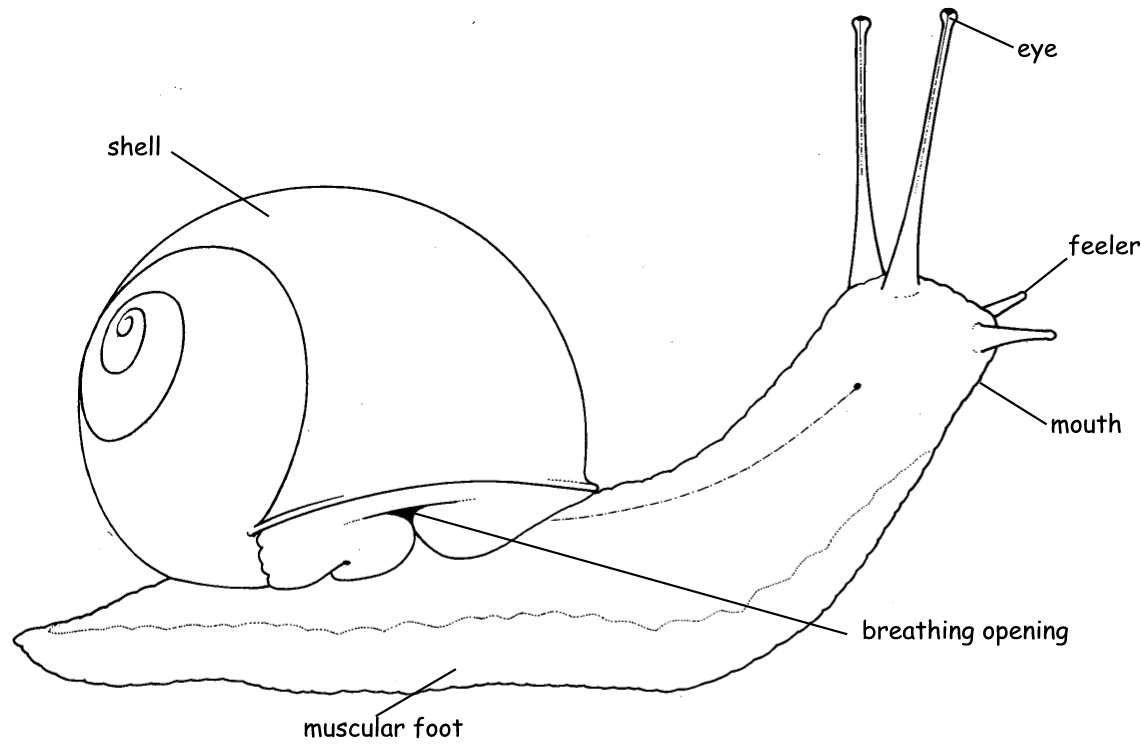
The body of the snail consists of a head, a foot and a hump. The hump contains the organs (for reproduction, digestion, etc.) and is covered by a shell. There is a spiracle under the shell on the right-hand side. Four tentacles are found on the head. Two have eyes while the other two serve as feelers. There is a T-shaped mouth underneath the head.
The snail moves by means of wavelike motions in the muscle foot. Slime is secreted, making the surface smooth.
The snail is plant eating and has a radula with which the plant material is grated fine.
Underneath the shell, the snail has a membrane that is rich in blood vessels (the mantle) and is used for breathing. The membrane connects to the air outside via the spiracle and thereby is protected from drying out.
The snail secretes slime that protects it from drying out. When the muscle foot is pulled into the shell, the only the part of the foot outside the shell is that part against the surface on which the snail is sitting. It therefore cannot dry out.
The snail lays eggs and the young look like the adults. Snails can have both male and female sexual cells and they keep them until conditions are favourable for the survival of the young.
The snail in the ecosystem
Snails eat plants and are an important link in various food chains. They are adapted very well to life on land and can survive dry conditions, although damp periods are essential for at least part of the year.
Assignments:
1. Describe what would happen in an ecosystem if people removed all the snails.
2. Make a summary of the ways in which the invertebrates that we have studied are adapted to survive in their particular environments by completing the table below:
| ANIMAL | FEEDING | RESPIRATION | WATER BALANCE |
| Earthworm | |||
| Grasshopper | |||
| Spider | |||
| Crab | |||
| Snail |
3. Research assignment : Describe how you would develop a corner of 100 square metres in a zoo into a self-sustaining zoo for invertebrates (in other words, the animals do not need to be fed). Your teacher will evaluate your project in terms of the following:
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to act confidently on curiosity about natural phenomena, and to investigate relationships and solve problems in scientific, technological and environmental contexts.
Assessment Standard 1.1: We know this when the learner plans investigations;
Assessment Standard 1.2: We know this when the learner conducts investigations and collects data;
Assessment Standard 1.3: We know this when the learner evaluates data and communicates findings.
Learning Outcome 2: The learner will know and be able to interpret and apply scientific, technological and environmental knowledge.
Assessment Standard 2.3: We know this when the learner interprets information;
Assessment Standard 2.4: We know this when the learner applies knowledge in a variation of a known situation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural sciences grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?