| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
(a) C 2 H 5 OH( l )
(b) Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 ( s )
(a)
(b)
Note: The standard state of carbon is graphite, and phosphorus exists as P 4 .
(a) C 2 H 5 OC 2 H 5 ( l )
(b) Na 2 CO 3 ( s )
(a) (b)
There are two ways to determine the amount of heat involved in a chemical change: measure it experimentally, or calculate it from other experimentally determined enthalpy changes. Some reactions are difficult, if not impossible, to investigate and make accurate measurements for experimentally. And even when a reaction is not hard to perform or measure, it is convenient to be able to determine the heat involved in a reaction without having to perform an experiment.
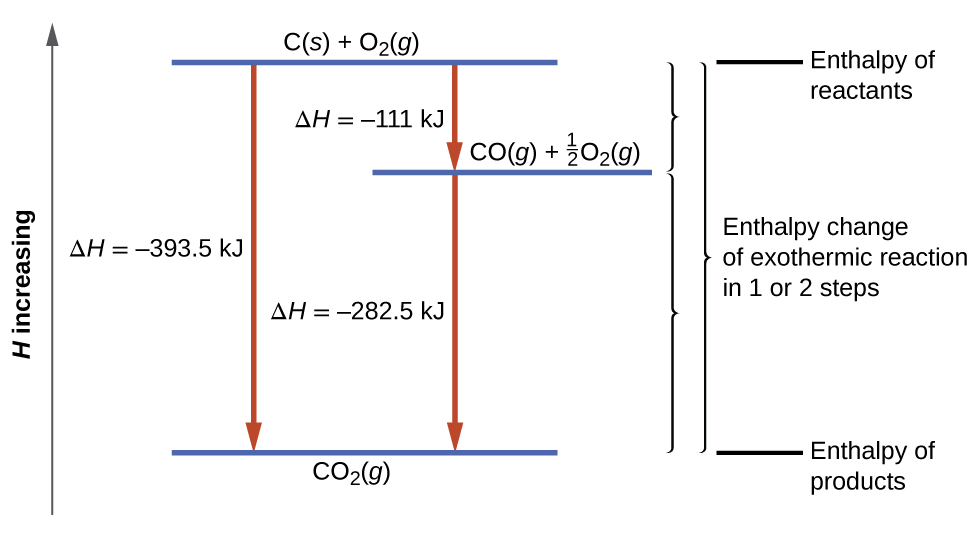
This type of calculation usually involves the use of Hess’s law , which states: If a process can be written as the sum of several stepwise processes, the enthalpy change of the total process equals the sum of the enthalpy changes of the various steps . Hess’s law is valid because enthalpy is a state function: Enthalpy changes depend only on where a chemical process starts and ends, but not on the path it takes from start to finish. For example, we can think of the reaction of carbon with oxygen to form carbon dioxide as occurring either directly or by a two-step process. The direct process is written:
In the two-step process, first carbon monoxide is formed:
Then, carbon monoxide reacts further to form carbon dioxide:
The equation describing the overall reaction is the sum of these two chemical changes:
Because the CO produced in Step 1 is consumed in Step 2, the net change is:
According to Hess’s law, the enthalpy change of the reaction will equal the sum of the enthalpy changes of the steps. We can apply the data from the experimental enthalpies of combustion in [link] to find the enthalpy change of the entire reaction from its two steps:
The result is shown in [link] . We see that Δ H of the overall reaction is the same whether it occurs in one step or two. This finding (overall Δ H for the reaction = sum of Δ H values for reaction “steps” in the overall reaction) is true in general for chemical and physical processes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?