| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The ionic polyhalides of the alkali metals, such as KI 3 , KICl 2 , KICl 4 , CsIBr 2 , and CsBrCl 2 , which contain an anion composed of at least three halogen atoms, are closely related to the interhalogens. As seen previously, the formation of the polyhalide anion is responsible for the solubility of iodine in aqueous solutions containing an iodide ion.
| Interhalogens | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| YX | YX 3 | YX 5 | YX 7 |
| ClF( g ) | ClF 3 ( g ) | ClF 5 ( g ) | |
| BrF( g ) | BrF 3 ( l ) | BrF 5 ( l ) | |
| BrCl( g ) | |||
| IF( s ) | IF 3 ( s ) | IF 5 ( l ) | IF 7 ( g ) |
| ICl( l ) | ICl 3 ( s ) | ||
| IBr( s ) |
The fluoride ion and fluorine compounds have many important uses. Compounds of carbon, hydrogen, and fluorine are replacing Freons (compounds of carbon, chlorine, and fluorine) as refrigerants. Teflon is a polymer composed of –CF 2 CF 2 – units. Fluoride ion is added to water supplies and to some toothpastes as SnF 2 or NaF to fight tooth decay. Fluoride partially converts teeth from Ca 5 (PO 4 ) 3 (OH) into Ca 5 (PO 4 ) 3 F.
Chlorine is important to bleach wood pulp and cotton cloth. The chlorine reacts with water to form hypochlorous acid, which oxidizes colored substances to colorless ones. Large quantities of chlorine are important in chlorinating hydrocarbons (replacing hydrogen with chlorine) to produce compounds such as tetrachloride (CCl 4 ), chloroform (CHCl 3 ), and ethyl chloride (C 2 H 5 Cl), and in the production of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and other polymers. Chlorine is also important to kill the bacteria in community water supplies.
Bromine is important in the production of certain dyes, and sodium and potassium bromides are used as sedatives. At one time, light-sensitive silver bromide was a component of photographic film.
Iodine in alcohol solution with potassium iodide is an antiseptic (tincture of iodine). Iodide salts are essential for the proper functioning of the thyroid gland; an iodine deficiency may lead to the development of a goiter. Iodized table salt contains 0.023% potassium iodide. Silver iodide is useful in the seeding of clouds to induce rain; it was important in the production of photographic film and iodoform, CHI 3 , is an antiseptic.
The halogens form halides with less electronegative elements. Halides of the metals vary from ionic to covalent; halides of nonmetals are covalent. Interhalogens form by the combination of two or more different halogens.
All of the representative metals react directly with elemental halogens or with solutions of the hydrohalic acids (HF, HCl, HBr, and HI) to produce representative metal halides. Other laboratory preparations involve the addition of aqueous hydrohalic acids to compounds that contain such basic anions, such as hydroxides, oxides, or carbonates.
What does it mean to say that mercury(II) halides are weak electrolytes?
Why is SnCl 4 not classified as a salt?
SnCl 4 is not a salt because it is covalently bonded. A salt must have ionic bonds.
The following reactions are all similar to those of the industrial chemicals. Complete and balance the equations for these reactions:
(a) reaction of a weak base and a strong acid
(b) preparation of a soluble silver salt for silver plating
(c) preparation of strontium hydroxide by electrolysis of a solution of strontium chloride
Which is the stronger acid, HClO 3 or HBrO 3 ? Why?
In oxyacids with similar formulas, the acid strength increases as the electronegativity of the central atom increases. HClO 3 is stronger than HBrO 3 ; Cl is more electronegative than Br.
What is the hybridization of iodine in IF 3 and IF 5 ?
Predict the molecular geometries and draw Lewis structures for each of the following. You may wish to review the chapter on chemical bonding and molecular geometry.
(a) IF 5
(b)
(c) PCl 5
(d) SeF 4
(e) ClF 3
(a)
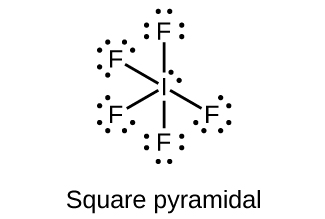 ;
;
(b)
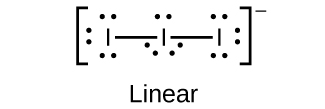 ;
;
(c)
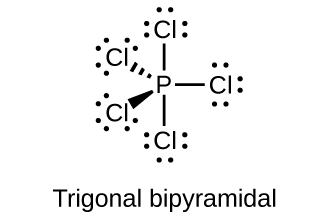 ;
;
(d)
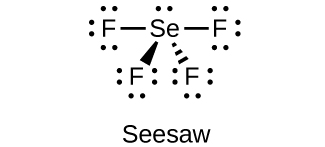 ;
;
(e)
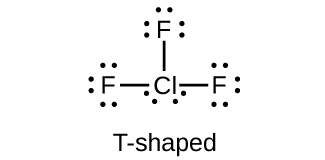
Which halogen has the highest ionization energy? Is this what you would predict based on what you have learned about periodic properties?
Name each of the following compounds:
(a) BrF 3
(b) NaBrO 3
(c) PBr 5
(d) NaClO 4
(e) KClO
(a) bromine trifluoride; (b) sodium bromate; (c) phosphorus pentabromide; (d) sodium perchlorate; (e) potassium hypochlorite
Explain why, at room temperature, fluorine and chlorine are gases, bromine is a liquid, and iodine is a solid.
What is the oxidation state of the halogen in each of the following?
(a) H 5 IO 6
(b)
(c) ClO 2
(d) ICl 3
(e) F 2
(a) I: 7+; (b) I: 7+; (c) Cl: 4+; (d) I: 3+; Cl: 1−; (e) F: 0
Physiological saline concentration—that is, the sodium chloride concentration in our bodies—is approximately 0.16 M . A saline solution for contact lenses is prepared to match the physiological concentration. If you purchase 25 mL of contact lens saline solution, how many grams of sodium chloride have you bought?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?