| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We can rank the strengths of acids by the extent to which they ionize in aqueous solution. The reaction of an acid with water is given by the general expression:
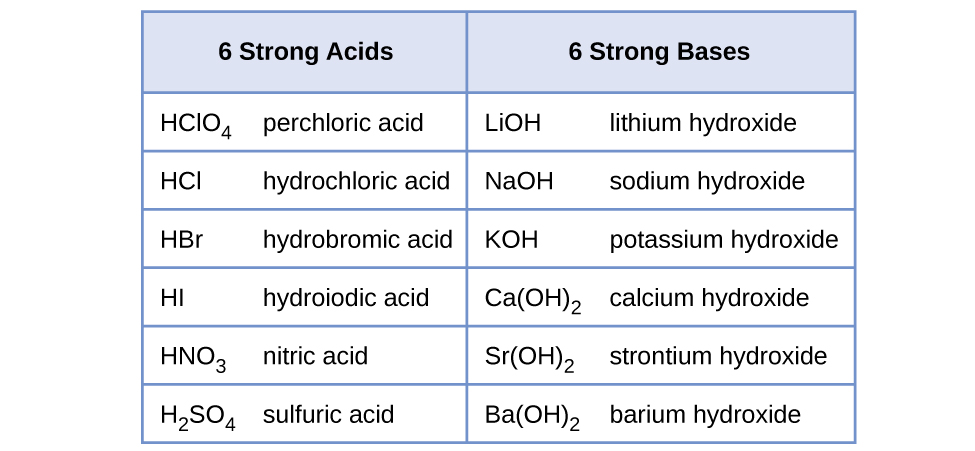
Water is the base that reacts with the acid HA, A − is the conjugate base of the acid HA, and the hydronium ion is the conjugate acid of water. A strong acid yields 100% (or very nearly so) of and A − when the acid ionizes in water; [link] lists several strong acids. A weak acid gives small amounts of and A − .
The relative strengths of acids may be determined by measuring their equilibrium constants in aqueous solutions. In solutions of the same concentration, stronger acids ionize to a greater extent, and so yield higher concentrations of hydronium ions than do weaker acids. The equilibrium constant for an acid is called the acid-ionization constant, K a . For the reaction of an acid HA:
we write the equation for the ionization constant as:
where the concentrations are those at equilibrium. Although water is a reactant in the reaction, it is the solvent as well, so we do not include [H 2 O] in the equation. The larger the K a of an acid, the larger the concentration of and A − relative to the concentration of the nonionized acid, HA. Thus a stronger acid has a larger ionization constant than does a weaker acid. The ionization constants increase as the strengths of the acids increase. (A table of ionization constants of weak acids appears in Appendix H , with a partial listing in [link] .)
The following data on acid-ionization constants indicate the order of acid strength CH 3 CO 2 H<HNO 2 <
Another measure of the strength of an acid is its percent ionization. The percent ionization of a weak acid is the ratio of the concentration of the ionized acid to the initial acid concentration, times 100:
Because the ratio includes the initial concentration, the percent ionization for a solution of a given weak acid varies depending on the original concentration of the acid, and actually decreases with increasing acid concentration.
The chemical equation for the dissociation of the nitrous acid is: Since 10 −pH = we find that 10 −2.09 = 8.1 10 −3 M , so that percent ionization is:
Remember, the logarithm 2.09 indicates a hydronium ion concentration with only two significant figures.
1.3% ionized

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?