| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When some substances are dissolved in water, they undergo either a physical or a chemical change that yields ions in solution. These substances constitute an important class of compounds called electrolytes . Substances that do not yield ions when dissolved are called nonelectrolytes . If the physical or chemical process that generates the ions is essentially 100% efficient (all of the dissolved compound yields ions), then the substance is known as a strong electrolyte . If only a relatively small fraction of the dissolved substance undergoes the ion-producing process, it is called a weak electrolyte .
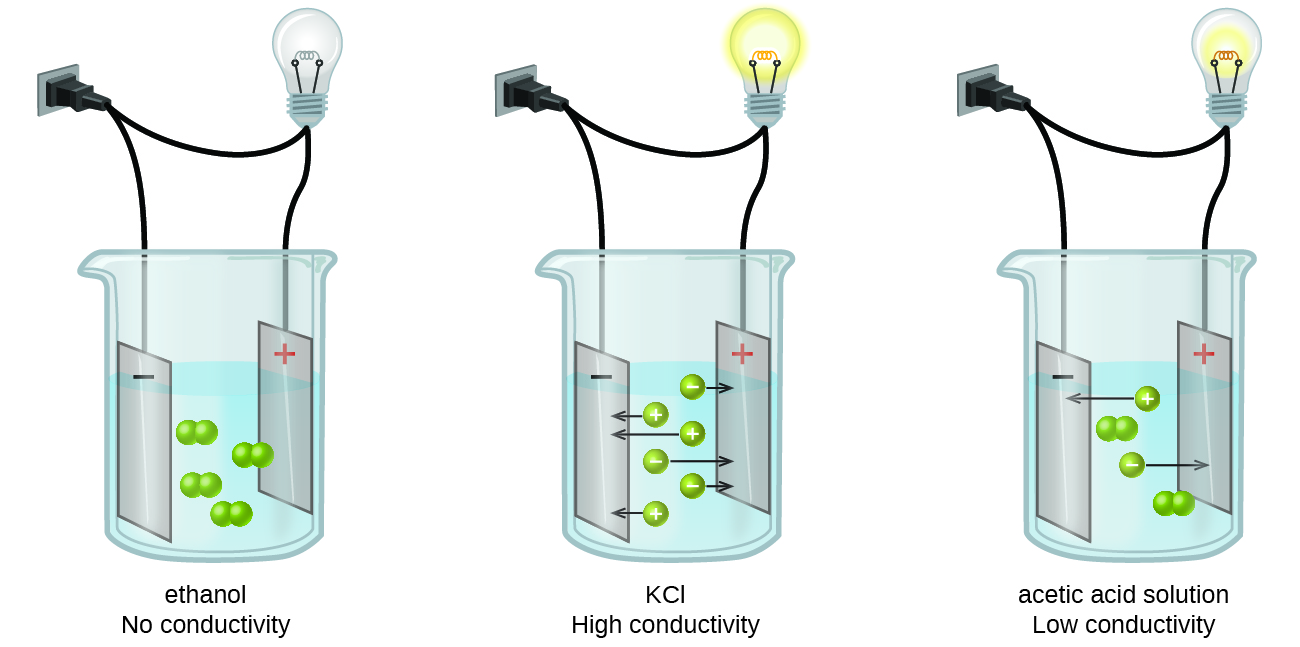
Substances may be identified as strong, weak, or nonelectrolytes by measuring the electrical conductance of an aqueous solution containing the substance. To conduct electricity, a substance must contain freely mobile, charged species. Most familiar is the conduction of electricity through metallic wires, in which case the mobile, charged entities are electrons. Solutions may also conduct electricity if they contain dissolved ions, with conductivity increasing as ion concentration increases. Applying a voltage to electrodes immersed in a solution permits assessment of the relative concentration of dissolved ions, either quantitatively, by measuring the electrical current flow, or qualitatively, by observing the brightness of a light bulb included in the circuit ( [link] ).
Water and other polar molecules are attracted to ions, as shown in [link] . The electrostatic attraction between an ion and a molecule with a dipole is called an ion-dipole attraction . These attractions play an important role in the dissolution of ionic compounds in water.
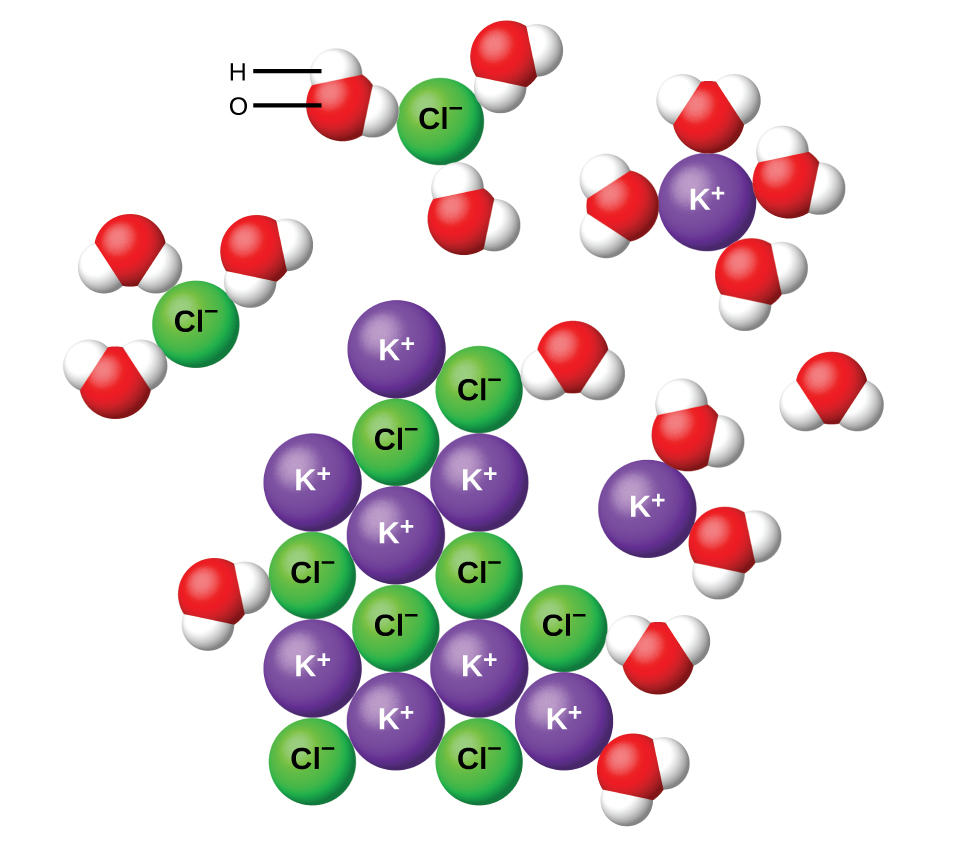
When ionic compounds dissolve in water, the ions in the solid separate and disperse uniformly throughout the solution because water molecules surround and solvate the ions, reducing the strong electrostatic forces between them. This process represents a physical change known as dissociation . Under most conditions, ionic compounds will dissociate nearly completely when dissolved, and so they are classified as strong electrolytes.
Let us consider what happens at the microscopic level when we add solid KCl to water. Ion-dipole forces attract the positive (hydrogen) end of the polar water molecules to the negative chloride ions at the surface of the solid, and they attract the negative (oxygen) ends to the positive potassium ions. The water molecules penetrate between individual K + and Cl − ions and surround them, reducing the strong interionic forces that bind the ions together and letting them move off into solution as solvated ions, as [link] shows. The reduction of the electrostatic attraction permits the independent motion of each hydrated ion in a dilute solution, resulting in an increase in the disorder of the system as the ions change from their fixed and ordered positions in the crystal to mobile and much more disordered states in solution. This increased disorder is responsible for the dissolution of many ionic compounds, including KCl, which dissolve with absorption of heat.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?