| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When most liquids are cooled, they eventually freeze and form crystalline solids , solids in which the atoms, ions, or molecules are arranged in a definite repeating pattern. It is also possible for a liquid to freeze before its molecules become arranged in an orderly pattern. The resulting materials are called amorphous solids or noncrystalline solids (or, sometimes, glasses). The particles of such solids lack an ordered internal structure and are randomly arranged ( [link] ).

Metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. Substances that consist of large molecules, or a mixture of molecules whose movements are more restricted, often form amorphous solids. For examples, candle waxes are amorphous solids composed of large hydrocarbon molecules. Some substances, such as boron oxide (shown in [link] ), can form either crystalline or amorphous solids, depending on the conditions under which it is produced. Also, amorphous solids may undergo a transition to the crystalline state under appropriate conditions.
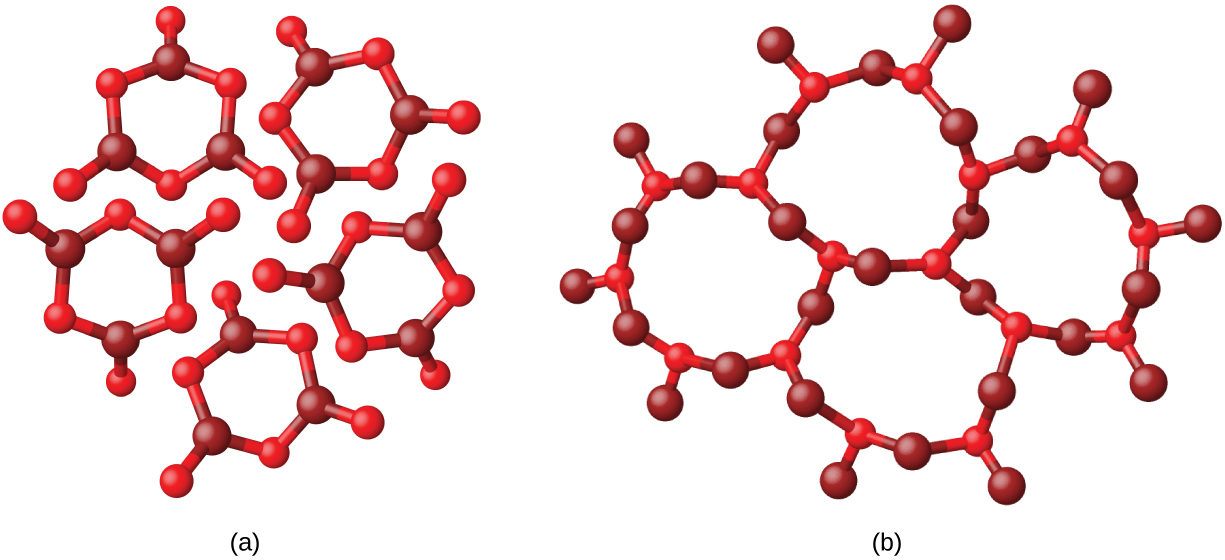
Crystalline solids are generally classified according the nature of the forces that hold its particles together. These forces are primarily responsible for the physical properties exhibited by the bulk solids. The following sections provide descriptions of the major types of crystalline solids: ionic, metallic, covalent network, and molecular.
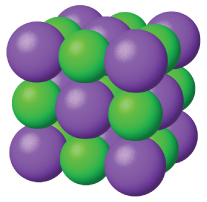
Ionic solids , such as sodium chloride and nickel oxide, are composed of positive and negative ions that are held together by electrostatic attractions, which can be quite strong ( [link] ). Many ionic crystals also have high melting points. This is due to the very strong attractions between the ions—in ionic compounds, the attractions between full charges are (much) larger than those between the partial charges in polar molecular compounds. This will be looked at in more detail in a later discussion of lattice energies. Although they are hard, they also tend to be brittle, and they shatter rather than bend. Ionic solids do not conduct electricity; however, they do conduct when molten or dissolved because their ions are free to move. Many simple compounds formed by the reaction of a metallic element with a nonmetallic element are ionic.
Metallic solids such as crystals of copper, aluminum, and iron are formed by metal atoms [link] . The structure of metallic crystals is often described as a uniform distribution of atomic nuclei within a “sea” of delocalized electrons. The atoms within such a metallic solid are held together by a unique force known as metallic bonding that gives rise to many useful and varied bulk properties. All exhibit high thermal and electrical conductivity, metallic luster, and malleability. Many are very hard and quite strong. Because of their malleability (the ability to deform under pressure or hammering), they do not shatter and, therefore, make useful construction materials. The melting points of the metals vary widely. Mercury is a liquid at room temperature, and the alkali metals melt below 200 °C. Several post-transition metals also have low melting points, whereas the transition metals melt at temperatures above 1000 °C. These differences reflect differences in strengths of metallic bonding among the metals.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?