| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
One of the most important types of motion in physics is simple harmonic motion, which is associated with such systems as an object with mass oscillating on a spring. Simple harmonic motion can be described by using either sine or cosine functions. In this section we expand our knowledge of derivative formulas to include derivatives of these and other trigonometric functions. We begin with the derivatives of the sine and cosine functions and then use them to obtain formulas for the derivatives of the remaining four trigonometric functions. Being able to calculate the derivatives of the sine and cosine functions will enable us to find the velocity and acceleration of simple harmonic motion.
We begin our exploration of the derivative for the sine function by using the formula to make a reasonable guess at its derivative. Recall that for a function
Consequently, for values of very close to 0, We see that by using
By setting and using a graphing utility, we can get a graph of an approximation to the derivative of ( [link] ).
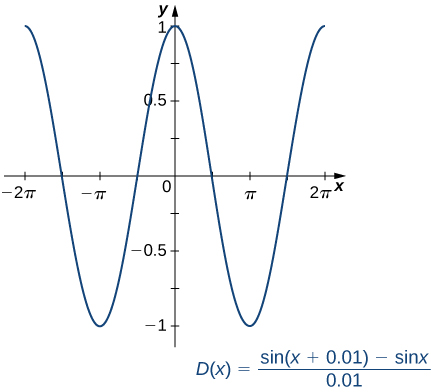
Upon inspection, the graph of appears to be very close to the graph of the cosine function. Indeed, we will show that
If we were to follow the same steps to approximate the derivative of the cosine function, we would find that
The derivative of the sine function is the cosine and the derivative of the cosine function is the negative sine.
Because the proofs for and use similar techniques, we provide only the proof for Before beginning, recall two important trigonometric limits we learned in Introduction to Limits :
The graphs of and are shown in [link] .
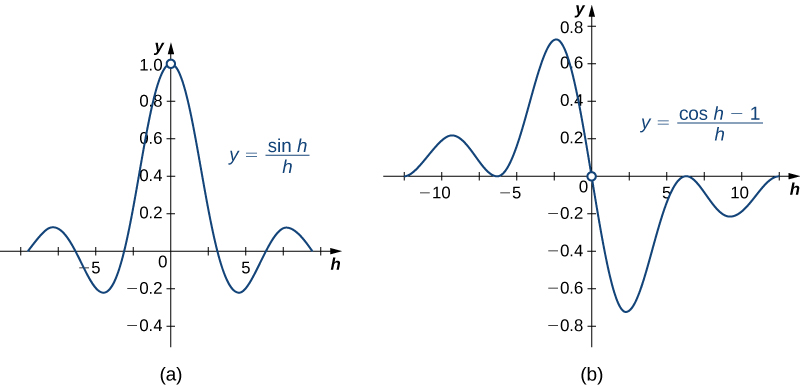
We also recall the following trigonometric identity for the sine of the sum of two angles:
Now that we have gathered all the necessary equations and identities, we proceed with the proof.
□
[link] shows the relationship between the graph of and its derivative Notice that at the points where has a horizontal tangent, its derivative takes on the value zero. We also see that where is increasing, and where is decreasing,

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?