| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
After studying this chapter, you will be able to:
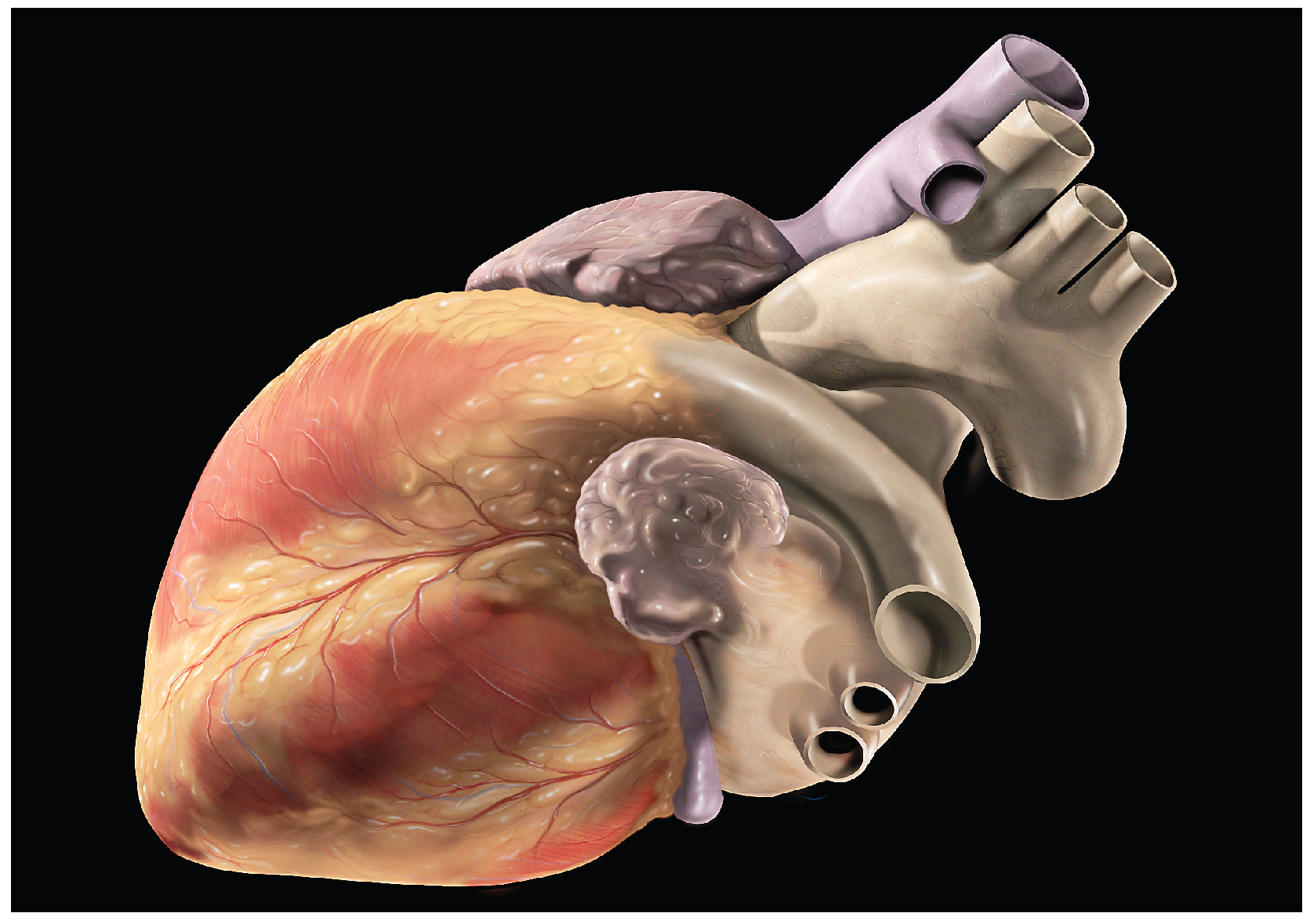
In this chapter, you will explore the remarkable pump that propels the blood into the vessels. There is no single better word to describe the function of the heart other than “pump,” since its contraction develops the pressure that ejects blood into the major vessels: the aorta and pulmonary trunk. From these vessels, the blood is distributed to the remainder of the body. Although the connotation of the term “pump” suggests a mechanical device made of steel and plastic, the anatomical structure is a living, sophisticated muscle. As you read this chapter, try to keep these twin concepts in mind: pump and muscle.
Although the term “heart” is an English word, cardiac (heart-related) terminology can be traced back to the Latin term, “kardia.” Cardiology is the study of the heart, and cardiologists are the physicians who deal primarily with the heart.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Human biology' conversation and receive update notifications?