| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
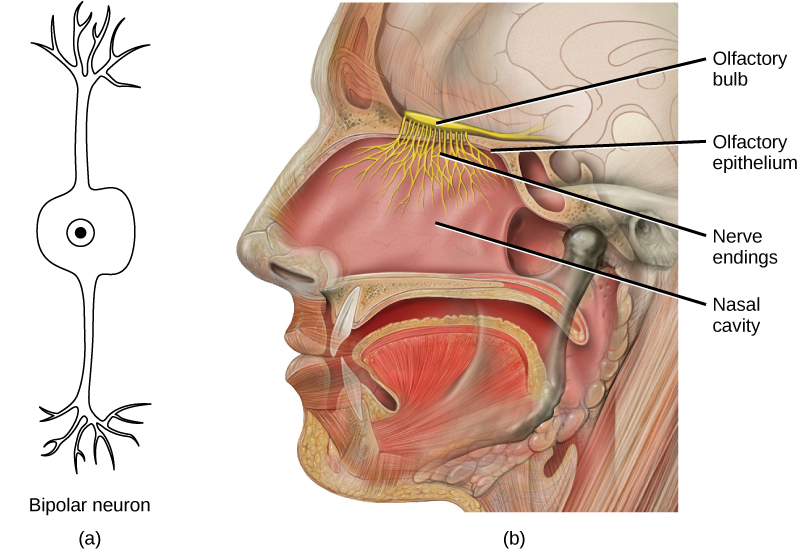
Olfactory neurons are bipolar neurons (neurons with two processes from the cell body). Each neuron has a single dendrite buried in the olfactory epithelium, and extending from this dendrite are 5 to 20 receptor-laden, hair-like cilia that trap odorant molecules. The sensory receptors on the cilia are proteins, and it is the variations in their amino acid chains that make the receptors sensitive to different odorants. Each olfactory sensory neuron has only one type of receptor on its cilia, and the receptors are specialized to detect specific odorants, so the bipolar neurons themselves are specialized. When an odorant binds with a receptor that recognizes it, the sensory neuron associated with the receptor is stimulated. Olfactory stimulation is the only sensory information that directly reaches the cerebral cortex, whereas other sensations are relayed through the thalamus.
The vomeronasal organ (VNO, or Jacobson’s organ) is a tubular, fluid-filled, olfactory organ present in many vertebrate animals that sits adjacent to the nasal cavity. It is very sensitive to pheromones and is connected to the nasal cavity by a duct. When molecules dissolve in the mucosa of the nasal cavity, they then enter the VNO where the pheromone molecules among them bind with specialized pheromone receptors. Upon exposure to pheromones from their own species or others, many animals, including cats, may display the flehmen response (shown in [link] ), a curling of the upper lip that helps pheromone molecules enter the VNO.
Pheromonal signals are sent, not to the main olfactory bulb, but to a different neural structure that projects directly to the amygdala (recall that the amygdala is a brain center important in emotional reactions, such as fear). The pheromonal signal then continues to areas of the hypothalamus that are key to reproductive physiology and behavior. While some scientists assert that the VNO is apparently functionally vestigial in humans, even though there is a similar structure located near human nasal cavities, others are researching it as a possible functional system that may, for example, contribute to synchronization of menstrual cycles in women living in close proximity.


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Human biology' conversation and receive update notifications?