| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
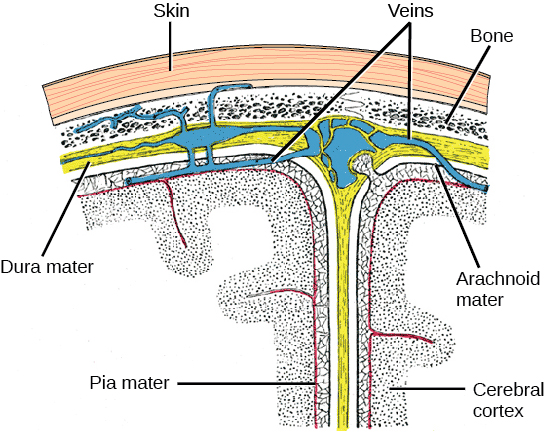
The central nervous system (CNS) is made up of the brain and spinal cord and is covered with three layers of protective coverings called meninges (“meninges” is derived from the Greek and means “membranes”) ( [link] ). The outermost layer is the dura mater, the middle layer is the web-like arachnoid mater, and the inner layer is the pia mater, which directly contacts and covers the brain and spinal cord. The space between the arachnoid and pia maters is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) . The brain floats in CSF, which acts as a cushion and shock absorber.
The brain is the part of the central nervous system that is contained in the cranial cavity of the skull. It includes the cerebral cortex, limbic system, basal ganglia, thalamus, hypothalamus, cerebellum, brainstem, and retinas. The outermost part of the brain is a thick piece of nervous system tissue called the cerebral cortex . The cerebral cortex, limbic system, and basal ganglia make up the two cerebral hemispheres. A thick fiber bundle called the corpus callosum (corpus = “body”; callosum = “tough”) connects the two hemispheres. Although there are some brain functions that are localized more to one hemisphere than the other, the functions of the two hemispheres are largely redundant. In fact, sometimes (very rarely) an entire hemisphere is removed to treat severe epilepsy. While patients do suffer some deficits following the surgery, they can have surprisingly few problems, especially when the surgery is performed on children who have very immature nervous systems.
In other surgeries to treat severe epilepsy, the corpus callosum is cut instead of removing an entire hemisphere. This causes a condition called split-brain, which gives insights into unique functions of the two hemispheres. For example, when an object is presented to patients’ left visual field, they may be unable to verbally name the object (and may claim to not have seen an object at all). This is because the visual input from the left visual field crosses and enters the right hemisphere and cannot then signal to the speech center, which generally is found in the left side of the brain. Remarkably, if a split-brain patient is asked to pick up a specific object out of a group of objects with the left hand, the patient will be able to do so but will still be unable to verbally identify it.
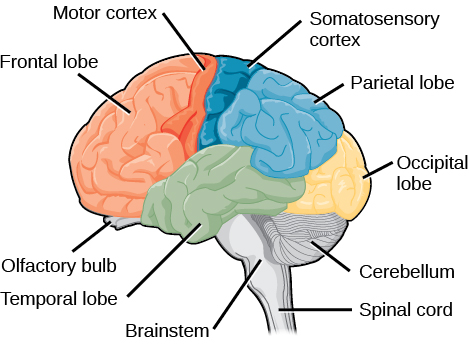
Each hemisphere contains regions called lobes that are involved in different functions. Each hemisphere of the mammalian cerebral cortex can be broken down into four functionally and spatially defined lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Human biology' conversation and receive update notifications?