| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The other major activity in the lungs is the process of respiration, the process of gas exchange. The function of respiration is to provide oxygen for use by body cells during cellular respiration and to eliminate carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular respiration, from the body. In order for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide to occur, both gases must be transported between the external and internal respiration sites. Both gases require a specialized transport system for the majority of the gas molecules to be moved between the lungs and other tissues.
The majority of oxygen molecules are carried from the lungs to the body’s tissues by a specialized transport system, which relies on the erythrocyte—the red blood cell. Erythrocytes contain hemoglobin, which serves to bind oxygen molecules to the erythrocyte ( [link] ). Heme is the portion of hemoglobin that contains iron, and it is heme that binds oxygen. One erythrocyte contains four iron ions, and because of this, each erythrocyte is capable of carrying up to four molecules of oxygen. As oxygen diffuses across the respiratory membrane from the alveolus to the capillary, it also diffuses into the red blood cell and is bound by hemoglobin. The following reversible chemical reaction describes the production of the final product, oxyhemoglobin (Hb–O 2 ), which is formed when oxygen binds to hemoglobin. Oxyhemoglobin is a bright red-colored molecule that contributes to the bright red color of oxygenated blood.
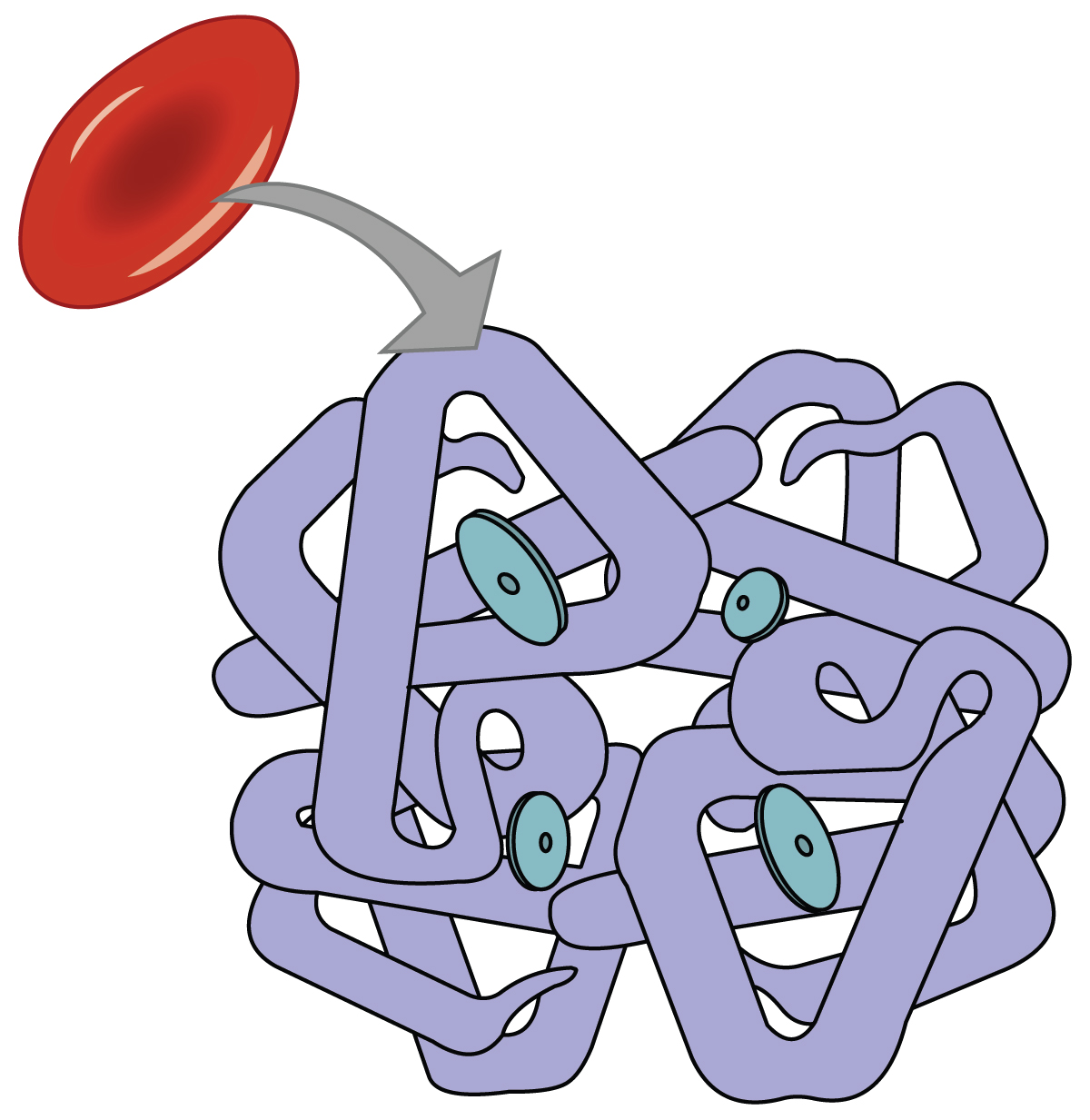
Hemoglobin is composed of subunits, a protein structure that is referred to as a quaternary structure. Each of the four subunits that make up hemoglobin is arranged in a ring-like fashion, with an iron atom covalently bound to the heme in the center of each subunit. When all four heme sites are occupied, the hemoglobin is said to be saturated. Hemoglobin saturation of 100 percent means that every heme unit in all of the erythrocytes of the body is bound to oxygen. In a healthy individual with normal hemoglobin levels, hemoglobin saturation generally ranges from 95 percent to 99 percent.
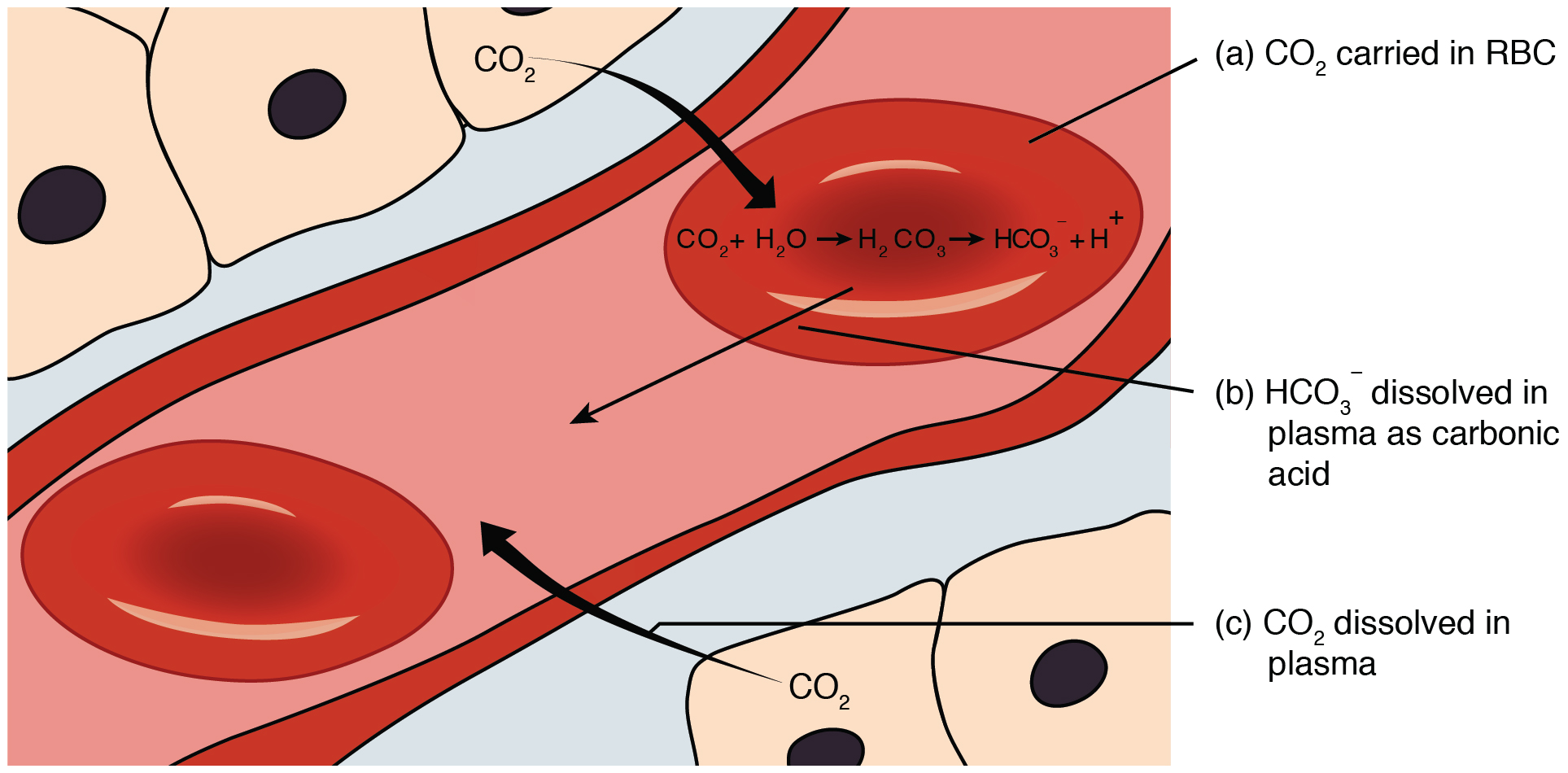
Carbon dioxide is transported by three major mechanisms. The first mechanism of carbon dioxide transport is by blood plasma, as some carbon dioxide molecules dissolve in the blood. The second mechanism is transport in the form of bicarbonate (HCO 3 – ), which also dissolves in plasma. The third mechanism of carbon dioxide transport is similar to the transport of oxygen by erythrocytes ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Human biology' conversation and receive update notifications?