| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
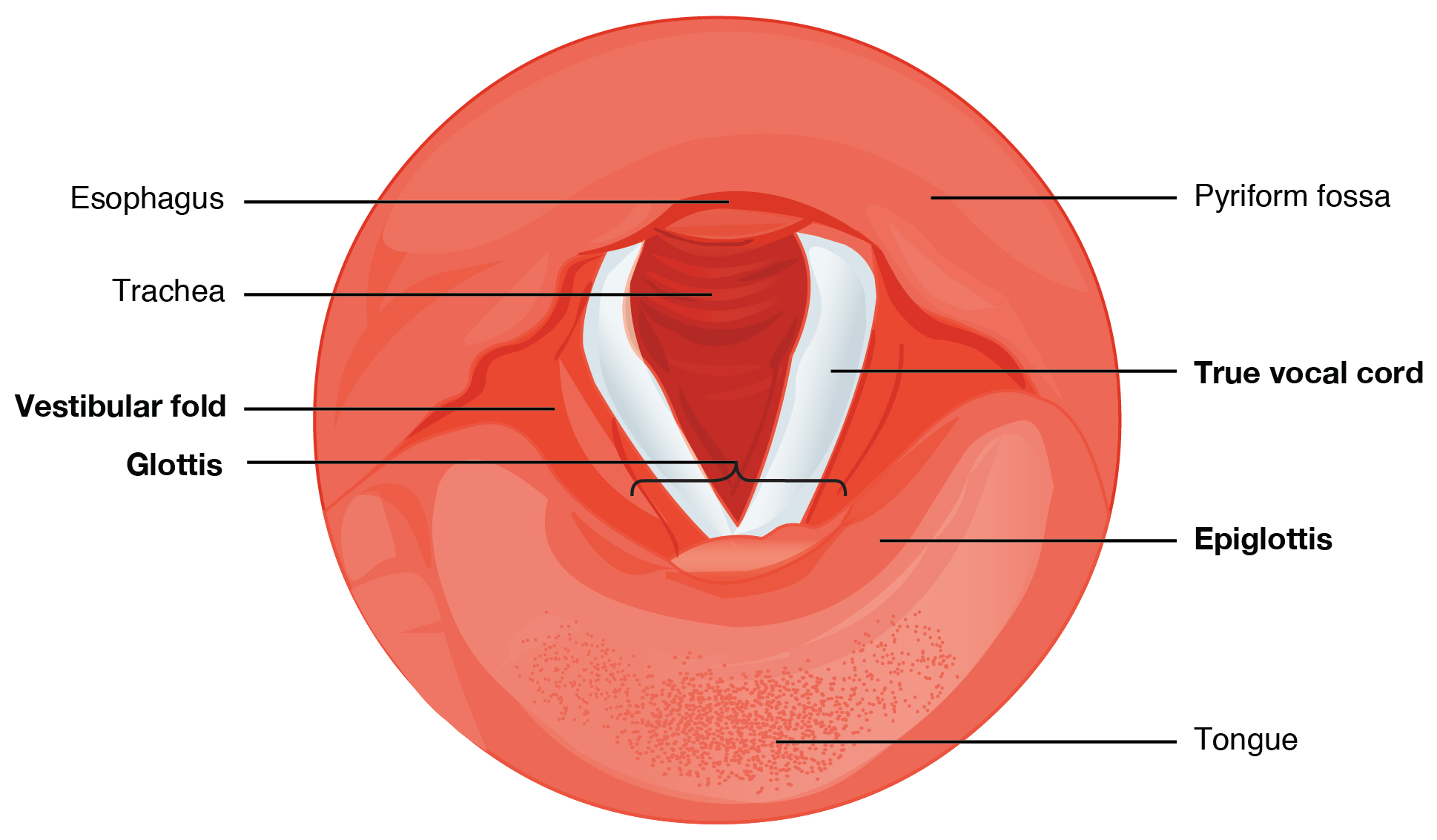
The trachea (windpipe) extends from the larynx toward the lungs ( [link] a ). The trachea is formed by 16 to 20 stacked pieces of cartilage that are connected by connective tissue. The fibroelastic membrane of the trachea allows it to stretch and expand slightly during inhalation and exhalation, whereas the rings of cartilage provide structural support and prevent the trachea from collapsing.
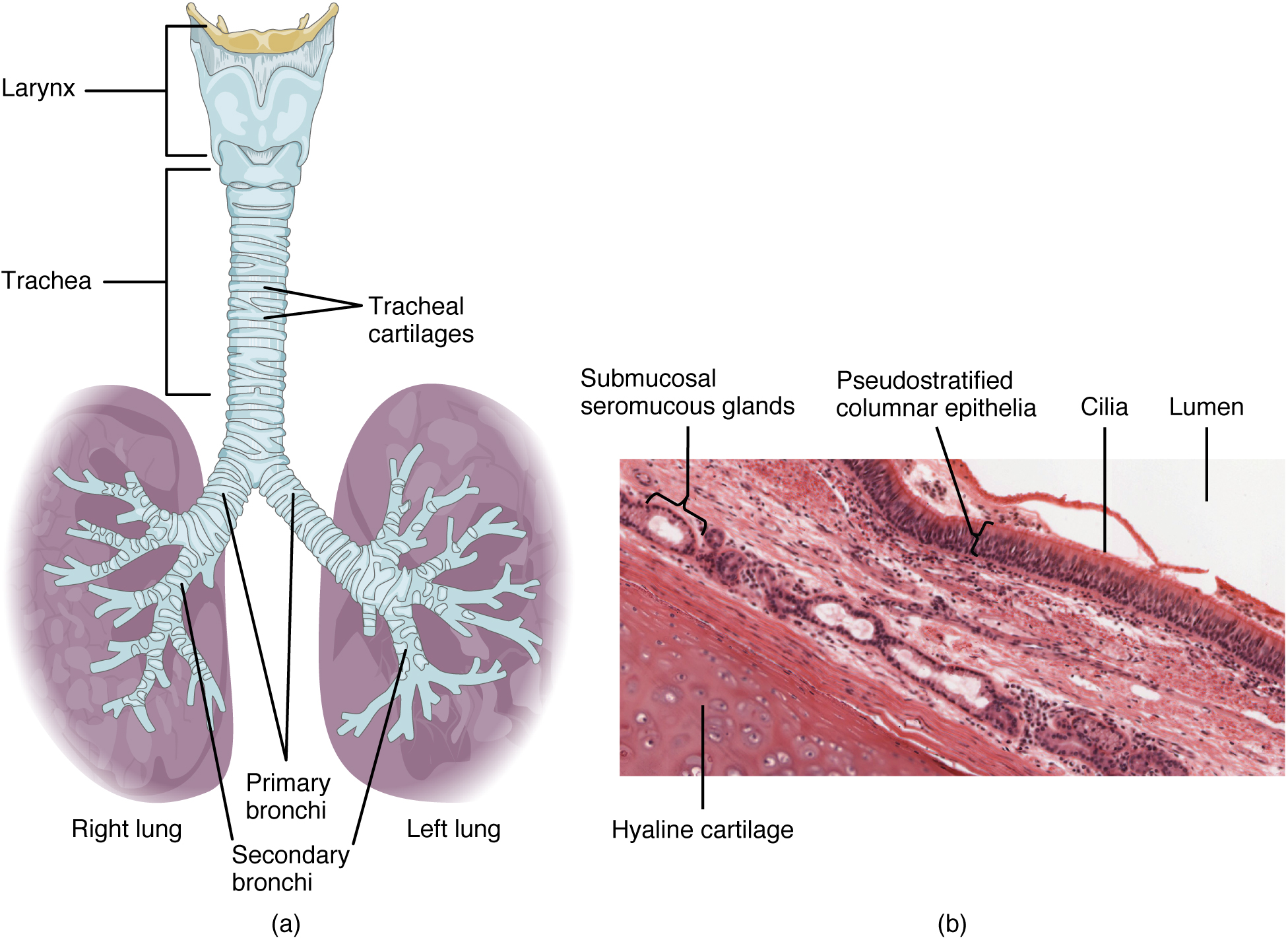
The right and left primary bronchi branch off the trachea towards the right and left lungs. The primary bronchi further branch into the secondary and tertiary bronchi. A bronchiole branches from the tertiary bronchi. Bronchioles, which are about 1 mm in diameter, further branch until they become the tiny terminal bronchioles, which lead to the structures of gas exchange. There are more than 1000 terminal bronchioles in each lung. The muscular walls of the bronchioles do not contain cartilage like those of the bronchi. However, smooth muscle can change the size of the tubing to increase or decrease airflow through it.
The respiratory zone includes structures that are directly involved in gas exchange. The respiratory zone begins where the terminal bronchioles join a respiratory bronchiole , the smallest type of bronchiole ( [link] ), which then leads to an alveolar duct, opening into a cluster of alveoli.
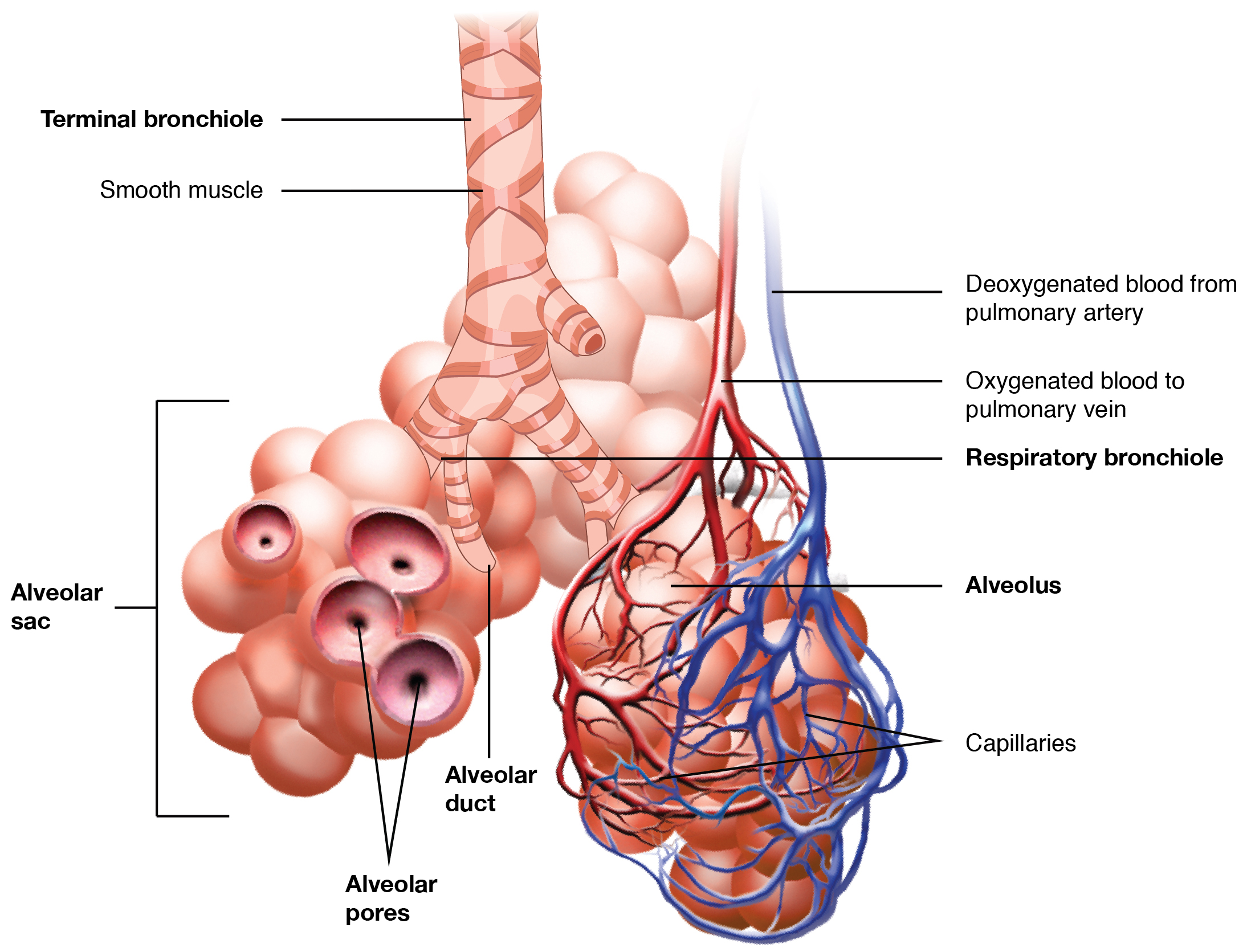
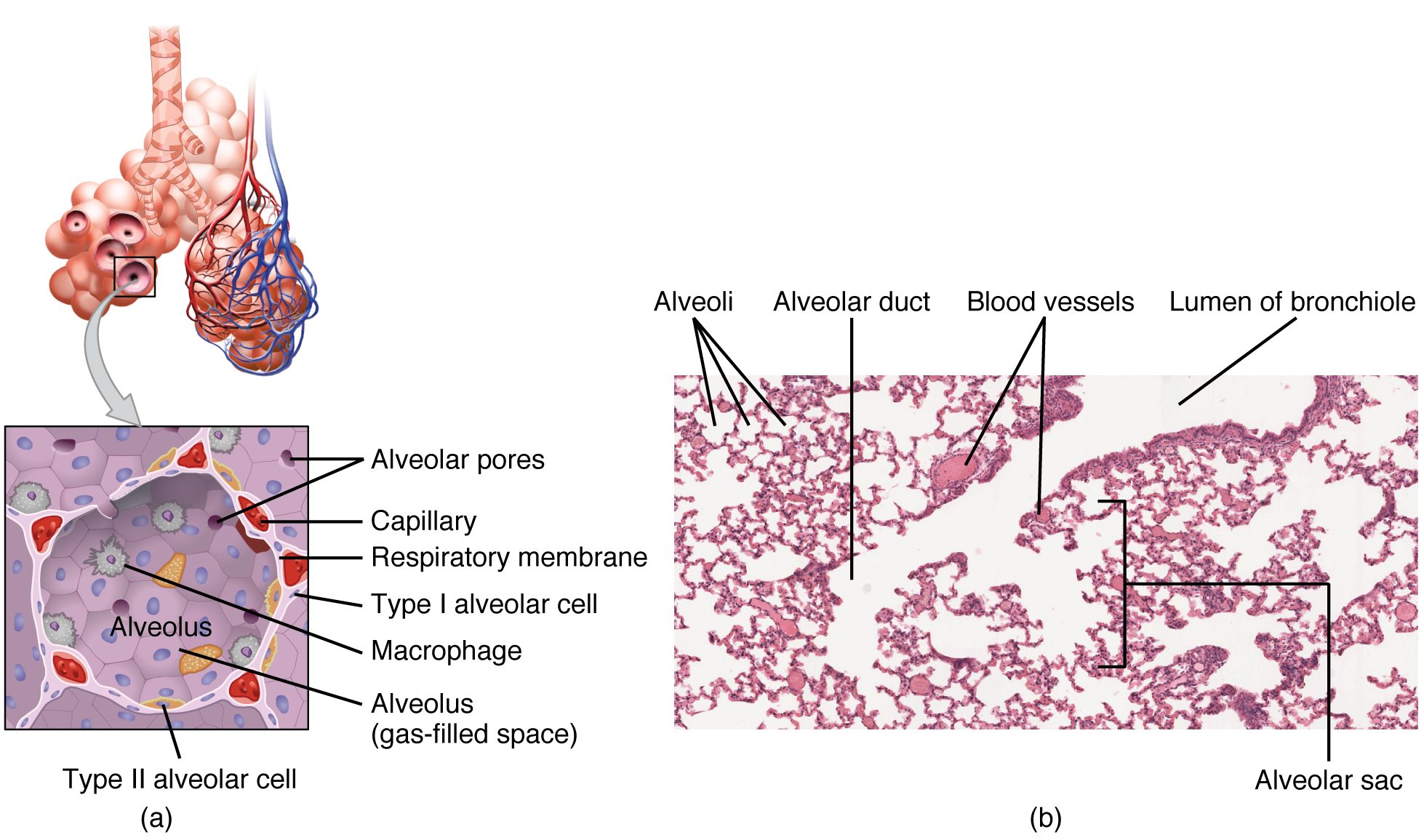
An alveolar sac is a cluster of many individual alveoli that are responsible for gas exchange. An alveolus is approximately 200 μm in diameter with elastic walls that allow the alveolus to stretch during air intake, which greatly increases the surface area available for gas exchange. Alveoli are connected to their neighbors by alveolar pores , which help maintain equal air pressure throughout the alveoli and lung ( [link] ).
Asthma is a chronic disease characterized by inflammation and fluid accumulation of the airway, and bronchospasms (that is, constriction of the bronchioles), which can inhibit air from entering the lungs. In addition, excessive mucus secretion can occur, which further contributes to blockage of the airway.
Bronchospasms occur periodically and lead to an “asthma attack.” An attack may be triggered by environmental factors such as dust, pollen, pet hair, or dander, changes in the weather, mold, tobacco smoke, and respiratory infections, or by exercise and stress.
Symptoms of an asthma attack involve coughing, shortness of breath, wheezing, and tightness of the chest. Symptoms of a severe asthma attack that requires immediate medical attention would include difficulty breathing that results in blue (cyanotic) lips or face, confusion, drowsiness, a rapid pulse, sweating, and severe anxiety. The severity of the condition, frequency of attacks, and identified triggers influence the type of medication that an individual may require. Longer-term treatments are used for those with more severe asthma. Short-term, fast-acting drugs that are used to treat an asthma attack are typically administered via an inhaler. For young children or individuals who have difficulty using an inhaler, asthma medications can be administered via a nebulizer.
Visit this site to learn more about what happens during an asthma attack. What are the three changes that occur inside the airways during an asthma attack?
Inflammation and the production of a thick mucus; constriction of the airway muscles, or bronchospasm; and an increased sensitivity to allergens.
Bizzintino J, Lee WM, Laing IA, Vang F, Pappas T, Zhang G, Martin AC, Khoo SK, Cox DW, Geelhoed GC, et al. Association between human rhinovirus C and severity of acute asthma in children. Eur Respir J [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2013 Mar 22]; 37(5):1037–1042. Available from: (External Link)&gca=erj%3B37%2F5%2F1037&allch=
Kumar V, Ramzi S, Robbins SL. Robbins Basic Pathology. 7th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier Ltd; 2005.
Martin RJ, Kraft M, Chu HW, Berns, EA, Cassell GH. A link between chronic asthma and chronic infection. J Allergy Clin Immunol [Internet]. 2001 [cited 2013 Mar 22]; 107(4):595-601. Available from: (External Link)&gca=erj%3B37%2F5%2F1037&allch=

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Human biology' conversation and receive update notifications?