| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Sharks reproduce sexually, and eggs are fertilized internally. Most species are ovoviviparous: The fertilized egg is retained in the oviduct of the mother’s body and the embryo is nourished by the egg yolk. The eggs hatch in the uterus, and young are born alive and fully functional. Some species of sharks are oviparous: They lay eggs that hatch outside of the mother’s body. Embryos are protected by a shark egg case or “mermaid’s purse” ( [link] ) that has the consistency of leather. The shark egg case has tentacles that snag in seaweed and give the newborn shark cover. A few species of sharks are viviparous: The young develop within the mother’s body and she gives live birth.

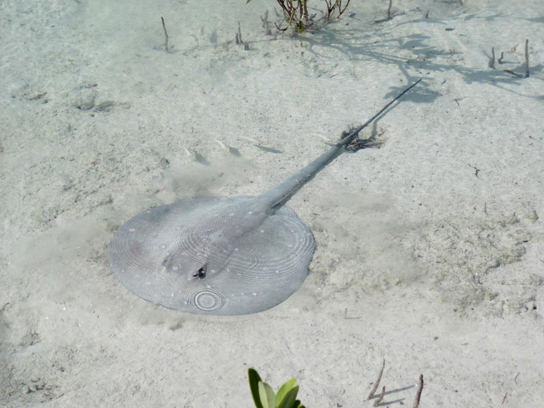
Rays and skates comprise more than 500 species and are closely related to sharks. They can be distinguished from sharks by their flattened bodies, pectoral fins that are enlarged and fused to the head, and gill slits on their ventral surface ( [link] ). Like sharks, rays and skates have a cartilaginous skeleton. Most species are marine and live on the sea floor, with nearly a worldwide distribution.

Members of the clade Osteichthyes , also called bony fishes, are characterized by a bony skeleton. The vast majority of present-day fishes belong to this group, which consists of approximately 30,000 species, making it the largest class of vertebrates in existence today.
Nearly all bony fishes have an ossified skeleton with specialized bone cells (osteocytes) that produce and maintain a calcium phosphate matrix. This characteristic has only reversed in a few groups of Osteichthyes, such as sturgeons and paddlefish, which have primarily cartilaginous skeletons. The skin of bony fishes is often covered by overlapping scales, and glands in the skin secrete mucus that reduces drag when swimming and aids the fish in osmoregulation. Like sharks, bony fishes have a lateral line system that detects vibrations in water.
All bony fishes use gills to breathe. Water is drawn over gills that are located in chambers covered and ventilated by a protective, muscular flap called the operculum. Many bony fishes also have a swim bladder , a gas-filled organ that helps to control the buoyancy of the fish. Bony fishes are further divided into two extant clades: Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) and Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fishes).
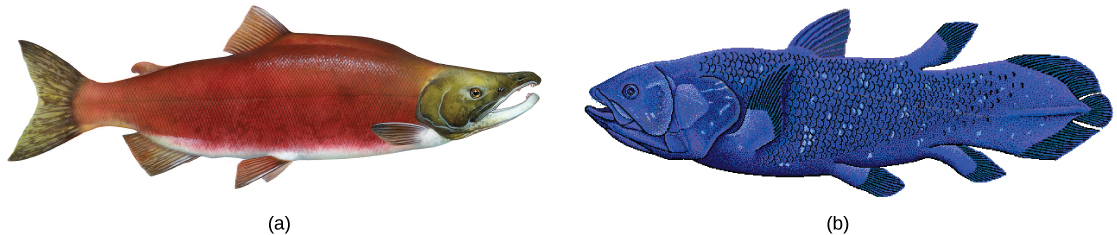
Actinopterygii, the ray-finned fishes, include many familiar fishes—tuna, bass, trout, and salmon ( [link] a ), among others. Ray-finned fishes are named for their fins that are webs of skin supported by bony spines called rays. In contrast, the fins of Sarcopterygii are fleshy and lobed, supported by bone ( [link] b ). Living members of this clade include the less-familiar lungfishes and coelacanths.
The earliest vertebrates that diverged from the invertebrate chordates were the jawless fishes. Fishes with jaws (gnathostomes) evolved later. Jaws allowed early gnathostomes to exploit new food sources. Agnathans include the hagfishes and lampreys. Hagfishes are eel-like scavengers that feed on dead invertebrates and other fishes. Lampreys are characterized by a toothed, funnel-like sucking mouth, and most species are parasitic on other fishes. Gnathostomes include the cartilaginous fishes and the bony fishes, as well as all other tetrapods. Cartilaginous fishes include sharks, rays, skates, and ghost sharks. Most cartilaginous fishes live in marine habitats, with a few species living in fresh water for part or all of their lives. The vast majority of present-day fishes belong to the clade Osteichthyes, which consists of approximately 30,000 species. Bony fishes can be divided into two clades: Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes, virtually all extant species) and Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fishes, comprising fewer than 10 extant species but which are the ancestors of tetrapods).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?