| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
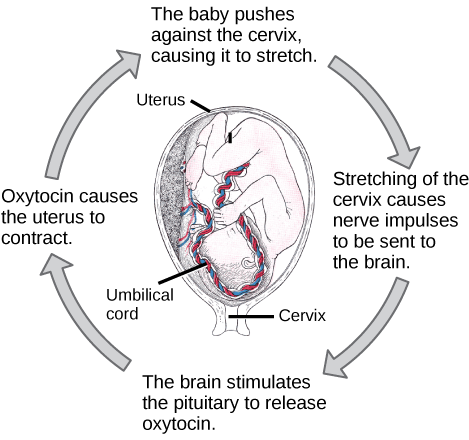
A positive feedback loop maintains the direction of the stimulus, possibly accelerating it. Few examples of positive feedback loops exist in animal bodies, but one is found in the cascade of chemical reactions that result in blood clotting, or coagulation. As one clotting factor is activated, it activates the next factor in sequence until a fibrin clot is achieved. The direction is maintained, not changed, so this is positive feedback. Another example of positive feedback is uterine contractions during childbirth, as illustrated in [link] . The hormone oxytocin, made by the endocrine system, stimulates the contraction of the uterus. This produces pain sensed by the nervous system. Instead of lowering the oxytocin and causing the pain to subside, more oxytocin is produced until the contractions are powerful enough to produce childbirth.
State whether each of the following processes is regulated by a positive feedback loop or a negative feedback loop.
It is possible to adjust a system’s set point. When this happens, the feedback loop works to maintain the new setting. An example of this is blood pressure: over time, the normal or set point for blood pressure can increase as a result of continued increases in blood pressure. The body no longer recognizes the elevation as abnormal and no attempt is made to return to the lower set point. The result is the maintenance of an elevated blood pressure that can have harmful effects on the body. Medication can lower blood pressure and lower the set point in the system to a more healthy level. This is called a process of alteration of the set point in a feedback loop.
Changes can be made in a group of body organ systems in order to maintain a set point in another system. This is called acclimatization . This occurs, for instance, when an animal migrates to a higher altitude than it is accustomed to. In order to adjust to the lower oxygen levels at the new altitude, the body increases the number of red blood cells circulating in the blood to ensure adequate oxygen delivery to the tissues. Another example of acclimatization is animals that have seasonal changes in their coats: a heavier coat in the winter ensures adequate heat retention, and a light coat in summer assists in keeping body temperature from rising to harmful levels.
Feedback mechanisms can be understood in terms of driving a race car along a track: watch a short video lesson on positive and negative feedback loops.
Body temperature affects body activities. Generally, as body temperature rises, enzyme activity rises as well. For every ten degree centigrade rise in temperature, enzyme activity doubles, up to a point. Body proteins, including enzymes, begin to denature and lose their function with high heat (around 50 o C for mammals). Enzyme activity will decrease by half for every ten degree centigrade drop in temperature, to the point of freezing, with a few exceptions. Some fish can withstand freezing solid and return to normal with thawing.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?