| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
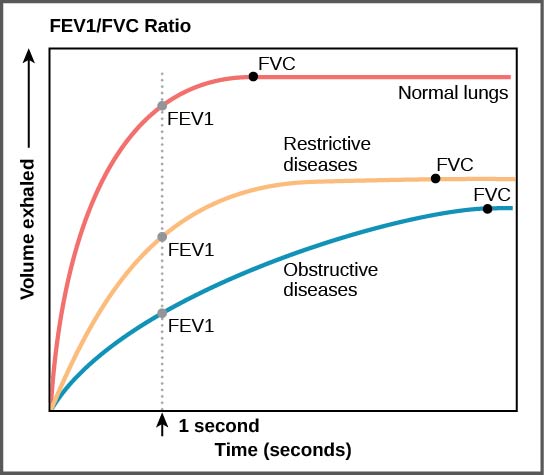
Examples of restrictive diseases are respiratory distress syndrome and pulmonary fibrosis. In both diseases, the airways are less compliant and they are stiff or fibrotic. There is a decrease in compliance because the lung tissue cannot bend and move. In these types of restrictive diseases, the intrapleural pressure is more positive and the airways collapse upon exhalation, which traps air in the lungs. Forced or functional vital capacity (FVC) , which is the amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled after taking the deepest breath possible, is much lower than in normal patients, and the time it takes to exhale most of the air is greatly prolonged ( [link] ). A patient suffering from these diseases cannot exhale the normal amount of air.
Obstructive diseases and conditions include emphysema, asthma, and pulmonary edema. In emphysema, which mostly arises from smoking tobacco, the walls of the alveoli are destroyed, decreasing the surface area for gas exchange. The overall compliance of the lungs is increased, because as the alveolar walls are damaged, lung elastic recoil decreases due to a loss of elastic fibers, and more air is trapped in the lungs at the end of exhalation. Asthma is a disease in which inflammation is triggered by environmental factors. Inflammation obstructs the airways. The obstruction may be due to edema (fluid accumulation), smooth muscle spasms in the walls of the bronchioles, increased mucus secretion, damage to the epithelia of the airways, or a combination of these events. Those with asthma or edema experience increased occlusion from increased inflammation of the airways. This tends to block the airways, preventing the proper movement of gases ( [link] ). Those with obstructive diseases have large volumes of air trapped after exhalation and breathe at a very high lung volume to compensate for the lack of airway recruitment.
Pulmonary circulation pressure is very low compared to that of the systemic circulation. It is also independent of cardiac output. This is because of a phenomenon called recruitment , which is the process of opening airways that normally remain closed when cardiac output increases. As cardiac output increases, the number of capillaries and arteries that are perfused (filled with blood) increases. These capillaries and arteries are not always in use but are ready if needed. At times, however, there is a mismatch between the amount of air (ventilation, V) and the amount of blood (perfusion, Q) in the lungs. This is referred to as ventilation/perfusion (V/Q) mismatch .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?