| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Female cones, or ovulate cones , contain two ovules per scale. One megaspore mother cell, or megasporocyte , undergoes meiosis in each ovule. Three of the four cells break down; only a single surviving cell will develop into a female multicellular gametophyte, which encloses archegonia (an archegonium is a reproductive organ that contains a single large egg). Upon fertilization, the diploid egg will give rise to the embryo, which is enclosed in a seed coat of tissue from the parent plant. Fertilization and seed development is a long process in pine trees: it may take up to two years after pollination. The seed that is formed contains three generations of tissues: the seed coat that originates from the sporophyte tissue, the gametophyte that will provide nutrients, and the embryo itself.
[link] illustrates the life cycle of a conifer. The sporophyte (2 n ) phase is the longest phase in the life of a gymnosperm. The gametophytes (1 n )—microspores and megaspores—are reduced in size. It may take more than year between pollination and fertilization while the pollen tube grows towards the megasporocyte (2 n ), which undergoes meiosis into megaspores. The megaspores will mature into eggs (1 n ).
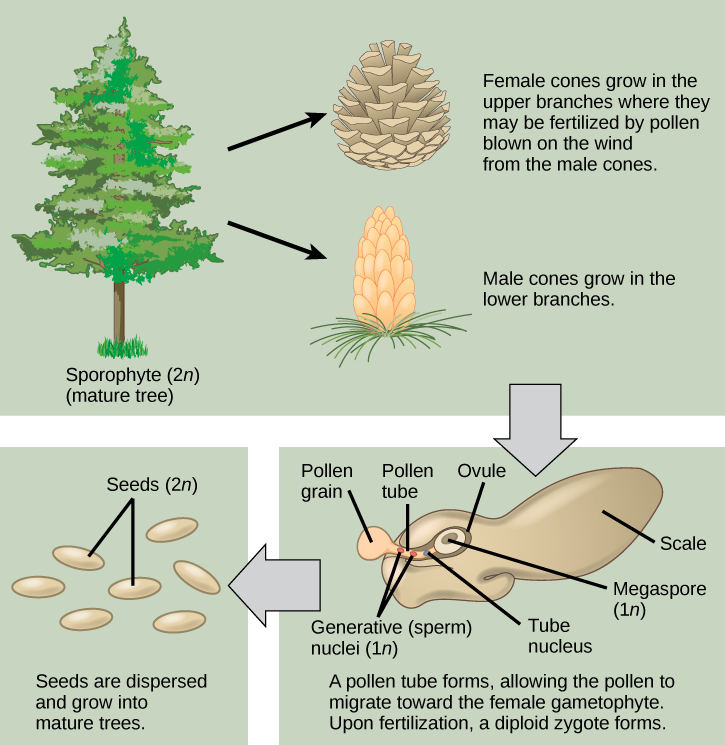
At what stage does the diploid zygote form?
Watch this video to see the process of seed production in gymnosperms.
Modern gymnosperms are classified into four phyla. Coniferophyta, Cycadophyta, and Ginkgophyta are similar in their production of secondary cambium (cells that generate the vascular system of the trunk or stem and are partially specialized for water transportation) and their pattern of seed development. However, the three phyla are not closely related phylogenetically to each other. Gnetophyta are considered the closest group to angiosperms because they produce true xylem tissue.
Conifers are the dominant phylum of gymnosperms, with the most variety of species ( [link] ). Most are typically tall trees that usually bear scale-like or needle-like leaves. Water evaporation from leaves is reduced by their thin shape and the thick cuticle. Snow slides easily off needle-shaped leaves, keeping the load light and decreasing breaking of branches. Adaptations to cold and dry weather explain the predominance of conifers at high altitudes and in cold climates. Conifers include familiar evergreen trees such as pines, spruces, firs, cedars, sequoias, and yews. A few species are deciduous and lose their leaves in fall. The European larch and the tamarack are examples of deciduous conifers ( [link] c ). Many coniferous trees are harvested for paper pulp and timber. The wood of conifers is more primitive than the wood of angiosperms; it contains tracheids, but no vessel elements, and is therefore referred to as “soft wood.”

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?