| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
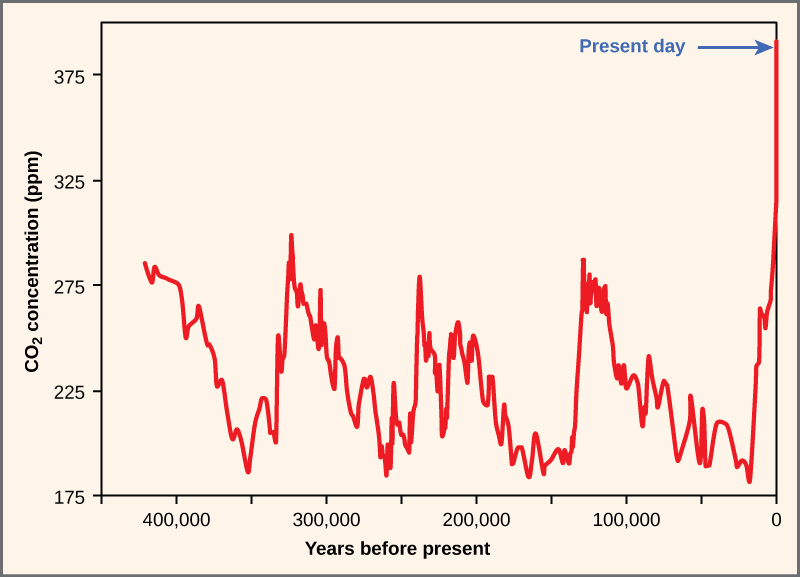
The core threat to biodiversity on the planet, and therefore a threat to human welfare, is the combination of human population growth and resource exploitation. The human population requires resources to survive and grow, and those resources are being removed unsustainably from the environment. The three greatest proximate threats to biodiversity are habitat loss, overharvesting, and introduction of exotic species. The first two of these are a direct result of human population growth and resource use. The third results from increased mobility and trade. A fourth major cause of extinction, anthropogenic climate change, has not yet had a large impact, but it is predicted to become significant during this century. Global climate change is also a consequence of human population needs for energy and the use of fossil fuels to meet those needs ( [link] ). Environmental issues, such as toxic pollution, have specific targeted effects on species, but they are not generally seen as threats at the magnitude of the others.
Humans rely on technology to modify their environment and replace certain functions that were once performed by the natural ecosystem. Other species cannot do this. Elimination of their ecosystem—whether it is a forest, a desert, a grassland, a freshwater estuarine, or a marine environment—will kill the individuals in the species. Remove the entire habitat within the range of a species and, unless they are one of the few species that do well in human-built environments, the species will become extinct. Human destruction of habitats accelerated in the latter half of the twentieth century. Consider the exceptional biodiversity of Sumatra: it is home to one species of orangutan, a species of critically endangered elephant, and the Sumatran tiger, but half of Sumatra’s forest is now gone. The neighboring island of Borneo, home to the other species of orangutan, has lost a similar area of forest. Forest loss continues in protected areas of Borneo. The orangutan in Borneo is listed as endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), but it is simply the most visible of thousands of species that will not survive the disappearance of the forests of Borneo. The forests are removed for timber and to plant palm oil plantations ( [link] ). Palm oil is used in many products including food products, cosmetics, and biodiesel in Europe. A five-year estimate of global forest cover loss for the years 2000–2005 was 3.1 percent. In the humid tropics where forest loss is primarily from timber extraction, 272,000 km 2 was lost out of a global total of 11,564,000 km 2 (or 2.4 percent). In the tropics, these losses certainly also represent the extinction of species because of high levels of endemism.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?