| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The immune system has to be regulated to prevent wasteful, unnecessary responses to harmless substances, and more importantly so that it does not attack “self.” The acquired ability to prevent an unnecessary or harmful immune response to a detected foreign substance known not to cause disease is described as immune tolerance . Immune tolerance is crucial for maintaining mucosal homeostasis given the tremendous number of foreign substances (such as food proteins) that APCs of the oral cavity, pharynx, and gastrointestinal mucosa encounter. Immune tolerance is brought about by specialized APCs in the liver, lymph nodes, small intestine, and lung that present harmless antigens to an exceptionally diverse population of regulatory T (T reg ) cells , specialized lymphocytes that suppress local inflammation and inhibit the secretion of stimulatory immune factors. The combined result of T reg cells is to prevent immunologic activation and inflammation in undesired tissue compartments and to allow the immune system to focus on pathogens instead. In addition to promoting immune tolerance of harmless antigens, other subsets of T reg cells are involved in the prevention of the autoimmune response , which is an inappropriate immune response to host cells or self-antigens. Another T reg class suppresses immune responses to harmful pathogens after the infection has cleared to minimize host cell damage induced by inflammation and cell lysis.
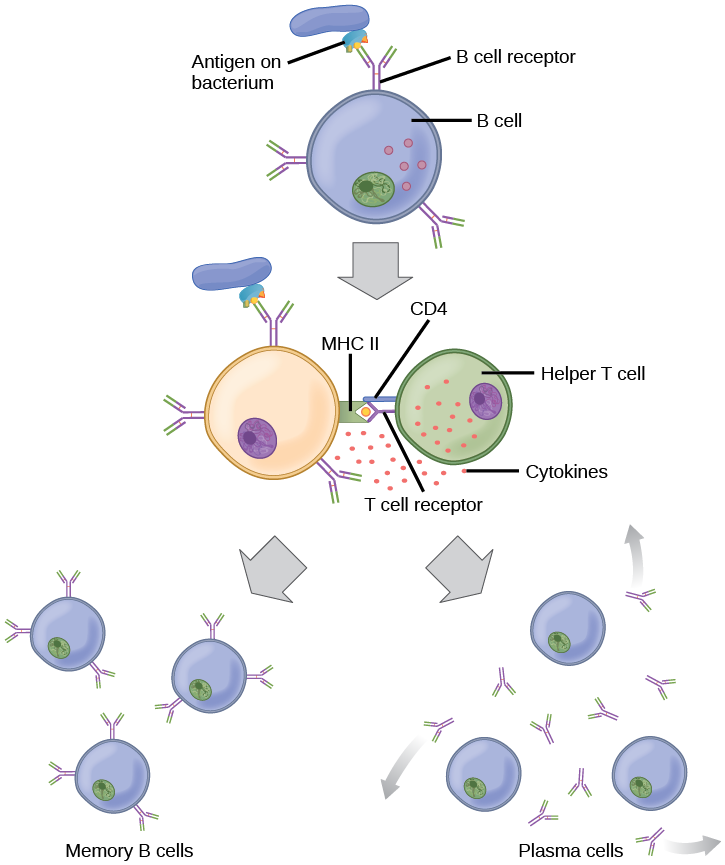
The adaptive immune system possesses a memory component that allows for an efficient and dramatic response upon reinvasion of the same pathogen. Memory is handled by the adaptive immune system with little reliance on cues from the innate response. During the adaptive immune response to a pathogen that has not been encountered before, called a primary response, plasma cells secreting antibodies and differentiated T cells increase, then plateau over time. As B and T cells mature into effector cells, a subset of the naïve populations differentiates into B and T memory cells with the same antigen specificities, as illustrated in [link] .
A memory cell is an antigen-specific B or T lymphocyte that does not differentiate into effector cells during the primary immune response, but that can immediately become effector cells upon re-exposure to the same pathogen. During the primary immune response, memory cells do not respond to antigens and do not contribute to host defenses. As the infection is cleared and pathogenic stimuli subside, the effectors are no longer needed, and they undergo apoptosis. In contrast, the memory cells persist in the circulation.
The Rh antigen is found on Rh-positive red blood cells. An Rh-negative female can usually carry an Rh-positive fetus to term without difficulty. However, if she has a second Rh-positive fetus, her body may launch an immune attack that causes hemolytic disease of the newborn. Why do you think hemolytic disease is only a problem during the second or subsequent pregnancies?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?