| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
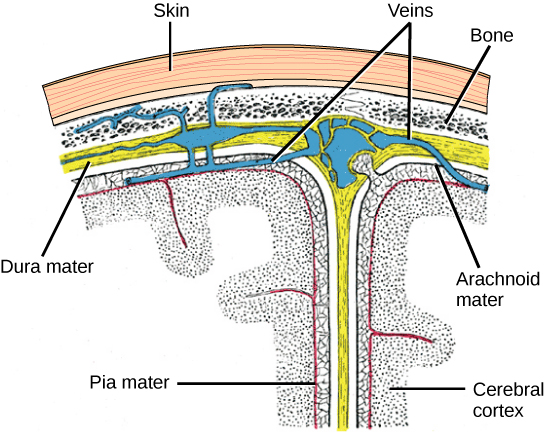
The central nervous system (CNS) is made up of the brain, a part of which is shown in [link] and spinal cord and is covered with three layers of protective coverings called meninges (from the Greek word for membrane). The outermost layer is the dura mater (Latin for “hard mother”). As the Latin suggests, the primary function for this thick layer is to protect the brain and spinal cord. The dura mater also contains vein-like structures that carry blood from the brain back to the heart. The middle layer is the web-like arachnoid mater . The last layer is the pia mater (Latin for “soft mother”), which directly contacts and covers the brain and spinal cord like plastic wrap. The space between the arachnoid and pia maters is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) . CSF is produced by a tissue called choroid plexus in fluid-filled compartments in the CNS called ventricles . The brain floats in CSF, which acts as a cushion and shock absorber and makes the brain neutrally buoyant. CSF also functions to circulate chemical substances throughout the brain and into the spinal cord.
The entire brain contains only about 8.5 tablespoons of CSF, but CSF is constantly produced in the ventricles. This creates a problem when a ventricle is blocked—the CSF builds up and creates swelling and the brain is pushed against the skull. This swelling condition is called hydrocephalus (“water head”) and can cause seizures, cognitive problems, and even death if a shunt is not inserted to remove the fluid and pressure.
The brain is the part of the central nervous system that is contained in the cranial cavity of the skull. It includes the cerebral cortex, limbic system, basal ganglia, thalamus, hypothalamus, and cerebellum. There are three different ways that a brain can be sectioned in order to view internal structures: a sagittal section cuts the brain left to right, as shown in [link] b , a coronal section cuts the brain front to back, as shown in [link] a , and a horizontal section cuts the brain top to bottom.
The outermost part of the brain is a thick piece of nervous system tissue called the cerebral cortex , which is folded into hills called gyri (singular: gyrus) and valleys called sulci (singular: sulcus). The cortex is made up of two hemispheres—right and left—which are separated by a large sulcus. A thick fiber bundle called the corpus callosum (Latin: “tough body”) connects the two hemispheres and allows information to be passed from one side to the other. Although there are some brain functions that are localized more to one hemisphere than the other, the functions of the two hemispheres are largely redundant. In fact, sometimes (very rarely) an entire hemisphere is removed to treat severe epilepsy. While patients do suffer some deficits following the surgery, they can have surprisingly few problems, especially when the surgery is performed on children who have very immature nervous systems.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?