| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
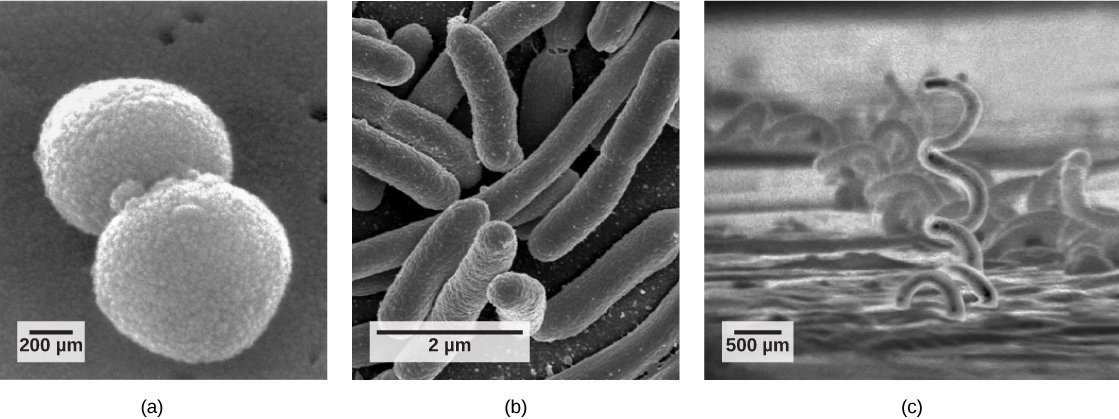
There are many differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. However, all cells have four common structures: the plasma membrane, which functions as a barrier for the cell and separates the cell from its environment; the cytoplasm, a jelly-like substance inside the cell; nucleic acids, the genetic material of the cell; and ribosomes, where protein synthesis takes place. Prokaryotes come in various shapes, but many fall into three categories: cocci (spherical), bacilli (rod-shaped), and spirilli (spiral-shaped) ( [link] ).
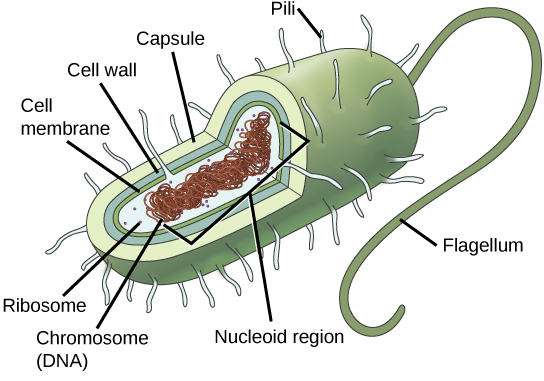
Recall that prokaryotes ( [link] ) are unicellular organisms that lack organelles or other internal membrane-bound structures. Therefore, they do not have a nucleus but instead generally have a single chromosome—a piece of circular, double-stranded DNA located in an area of the cell called the nucleoid. Most prokaryotes have a cell wall outside the plasma membrane.
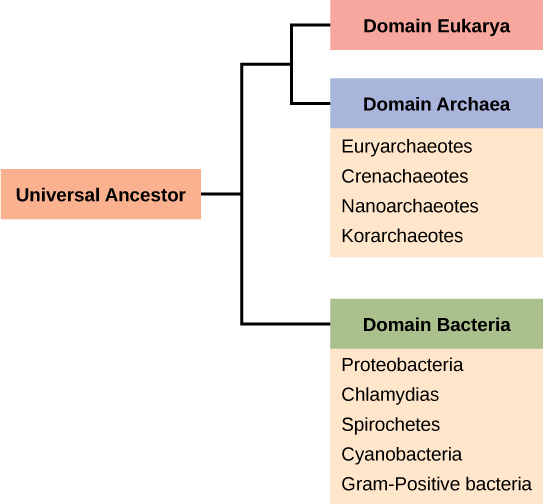
Recall that prokaryotes are divided into two different domains, Bacteria and Archaea, which together with Eukarya, comprise the three domains of life ( [link] ).
The composition of the cell wall differs significantly between the domains Bacteria and Archaea. The composition of their cell walls also differs from the eukaryotic cell walls found in plants (cellulose) or fungi and insects (chitin). The cell wall functions as a protective layer, and it is responsible for the organism’s shape. Some bacteria have an outer capsule outside the cell wall. Other structures are present in some prokaryotic species, but not in others ( [link] ). For example, the capsule found in some species enables the organism to attach to surfaces, protects it from dehydration and attack by phagocytic cells, and makes pathogens more resistant to our immune responses. Some species also have flagella (singular, flagellum) used for locomotion, and pili (singular, pilus) used for attachment to surfaces. Plasmids, which consist of extra-chromosomal DNA, are also present in many species of bacteria and archaea.
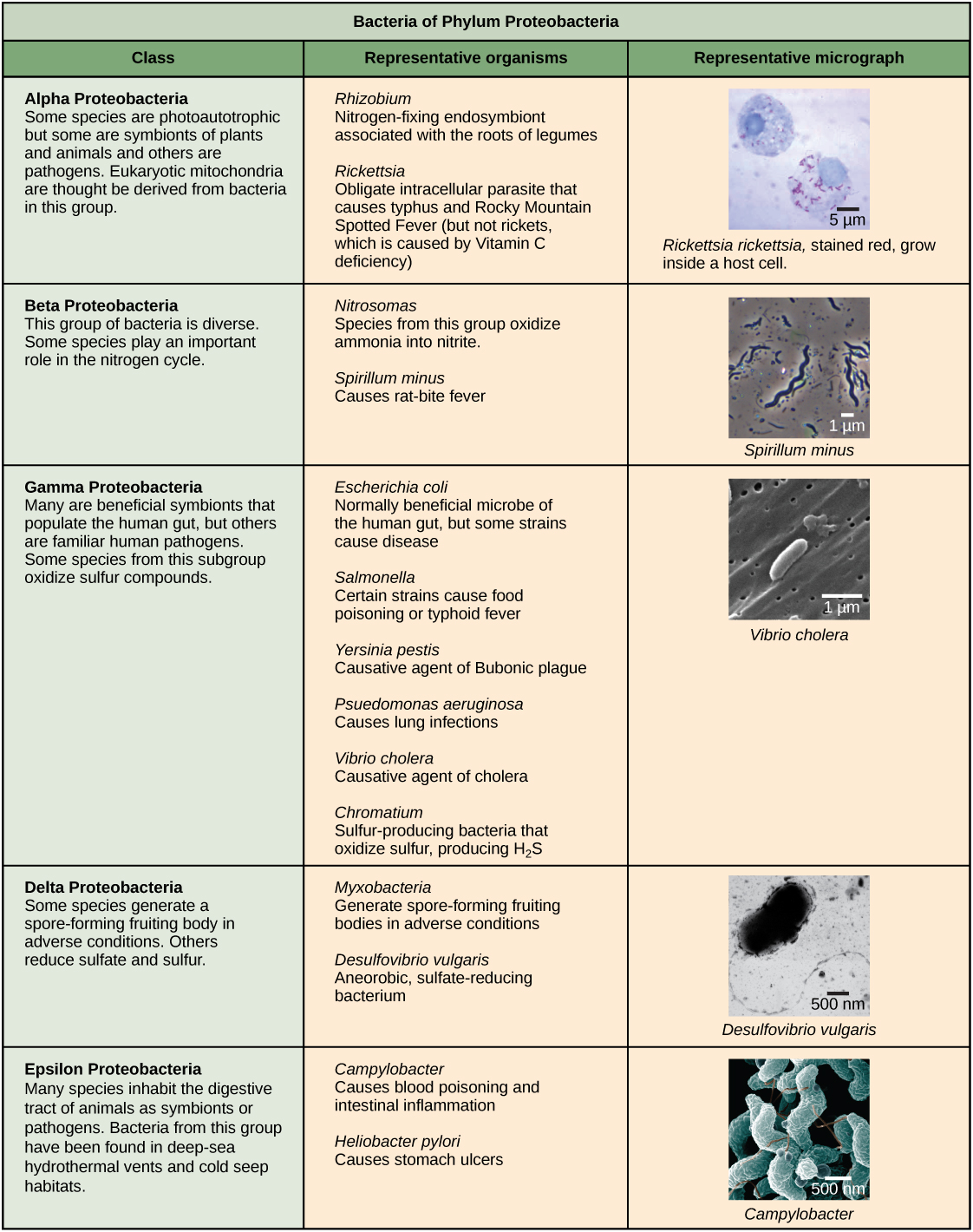
Characteristics of phyla of Bacteria are described in [link] and [link] ; Archaea are described in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?