| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The third life-cycle type, employed by some algae and all plants, is a blend of the haploid-dominant and diploid-dominant extremes. Species with alternation of generations have both haploid and diploid multicellular organisms as part of their life cycle. The haploid multicellular plants are called gametophytes , because they produce gametes from specialized cells. Meiosis is not directly involved in the production of gametes in this case, because the organism that produces the gametes is already a haploid. Fertilization between the gametes forms a diploid zygote. The zygote will undergo many rounds of mitosis and give rise to a diploid multicellular plant called a sporophyte . Specialized cells of the sporophyte will undergo meiosis and produce haploid spores. The spores will subsequently develop into the gametophytes ( [link] ).
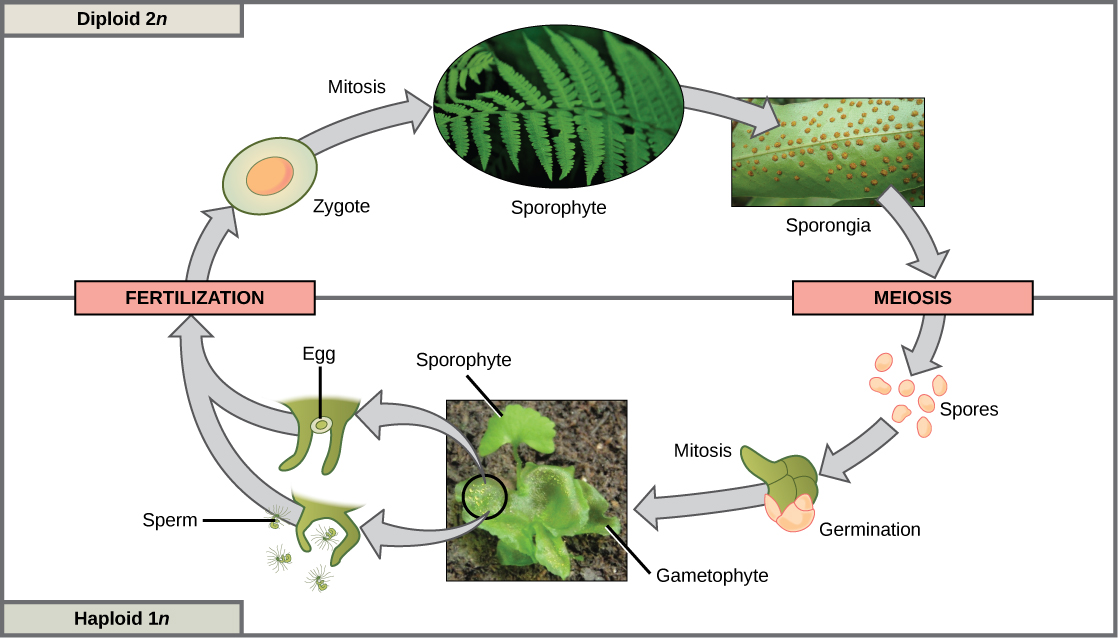
Although all plants utilize some version of the alternation of generations, the relative size of the sporophyte and the gametophyte and the relationship between them vary greatly. In plants such as moss, the gametophyte organism is the free-living plant, and the sporophyte is physically dependent on the gametophyte. In other plants, such as ferns, both the gametophyte and sporophyte plants are free-living; however, the sporophyte is much larger. In seed plants, such as magnolia trees and daisies, the gametophyte is composed of only a few cells and, in the case of the female gametophyte, is completely retained within the sporophyte.
Sexual reproduction takes many forms in multicellular organisms. However, at some point in each type of life cycle, meiosis produces haploid cells that will fuse with the haploid cell of another organism. The mechanisms of variation—crossover, random assortment of homologous chromosomes, and random fertilization—are present in all versions of sexual reproduction. The fact that nearly every multicellular organism on Earth employs sexual reproduction is strong evidence for the benefits of producing offspring with unique gene combinations, though there are other possible benefits as well.
Nearly all eukaryotes undergo sexual reproduction. The variation introduced into the reproductive cells by meiosis appears to be one of the advantages of sexual reproduction that has made it so successful. Meiosis and fertilization alternate in sexual life cycles. The process of meiosis produces unique reproductive cells called gametes, which have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Fertilization, the fusion of haploid gametes from two individuals, restores the diploid condition. Thus, sexually reproducing organisms alternate between haploid and diploid stages. However, the ways in which reproductive cells are produced and the timing between meiosis and fertilization vary greatly. There are three main categories of life cycles: diploid-dominant, demonstrated by most animals; haploid-dominant, demonstrated by all fungi and some algae; and the alternation of generations, demonstrated by plants and some algae.
[link] If a mutation occurs so that a fungus is no longer able to produce a minus mating type, will it still be able to reproduce?
[link] Yes, it will be able to reproduce asexually.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?