| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Thanks to mass loss, then, stars with starting masses up to at least 8 M Sun (and perhaps even more) probably end their lives as white dwarfs. But we know stars can have masses as large as 150 (or more) M Sun . They have a different kind of death in store for them. As we will see, these stars die with a bang.
After the helium in its core is exhausted (see The Evolution of More Massive Stars ), the evolution of a massive star takes a significantly different course from that of lower-mass stars. In a massive star, the weight of the outer layers is sufficient to force the carbon core to contract until it becomes hot enough to fuse carbon into oxygen, neon, and magnesium. This cycle of contraction, heating, and the ignition of another nuclear fuel repeats several more times. After each of the possible nuclear fuels is exhausted, the core contracts again until it reaches a new temperature high enough to fuse still-heavier nuclei. The products of carbon fusion can be further converted into silicon, sulfur, calcium, and argon. And these elements, when heated to a still-higher temperature, can combine to produce iron. Massive stars go through these stages very, very quickly. In really massive stars, some fusion stages toward the very end can take only months or even days! This is a far cry from the millions of years they spend in the main-sequence stage.
At this stage of its evolution, a massive star resembles an onion with an iron core. As we get farther from the center, we find shells of decreasing temperature in which nuclear reactions involve nuclei of progressively lower mass—silicon and sulfur, oxygen, neon, carbon, helium, and finally, hydrogen ( [link] ).
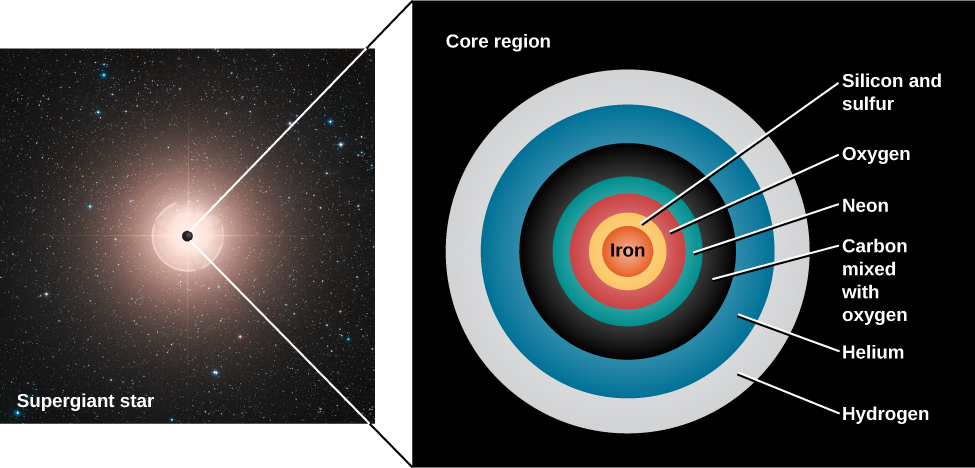
But there is a limit to how long this process of building up elements by fusion can go on. The fusion of silicon into iron turns out to be the last step in the sequence of nonexplosive element production. Up to this point, each fusion reaction has produced energy because the nucleus of each fusion product has been a bit more stable than the nuclei that formed it. As discussed in The Sun: A Nuclear Powerhouse , light nuclei give up some of their binding energy in the process of fusing into more tightly bound, heavier nuclei. It is this released energy that maintains the outward pressure in the core so that the star does not collapse. But of all the nuclei known, iron is the most tightly bound and thus the most stable.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?