| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
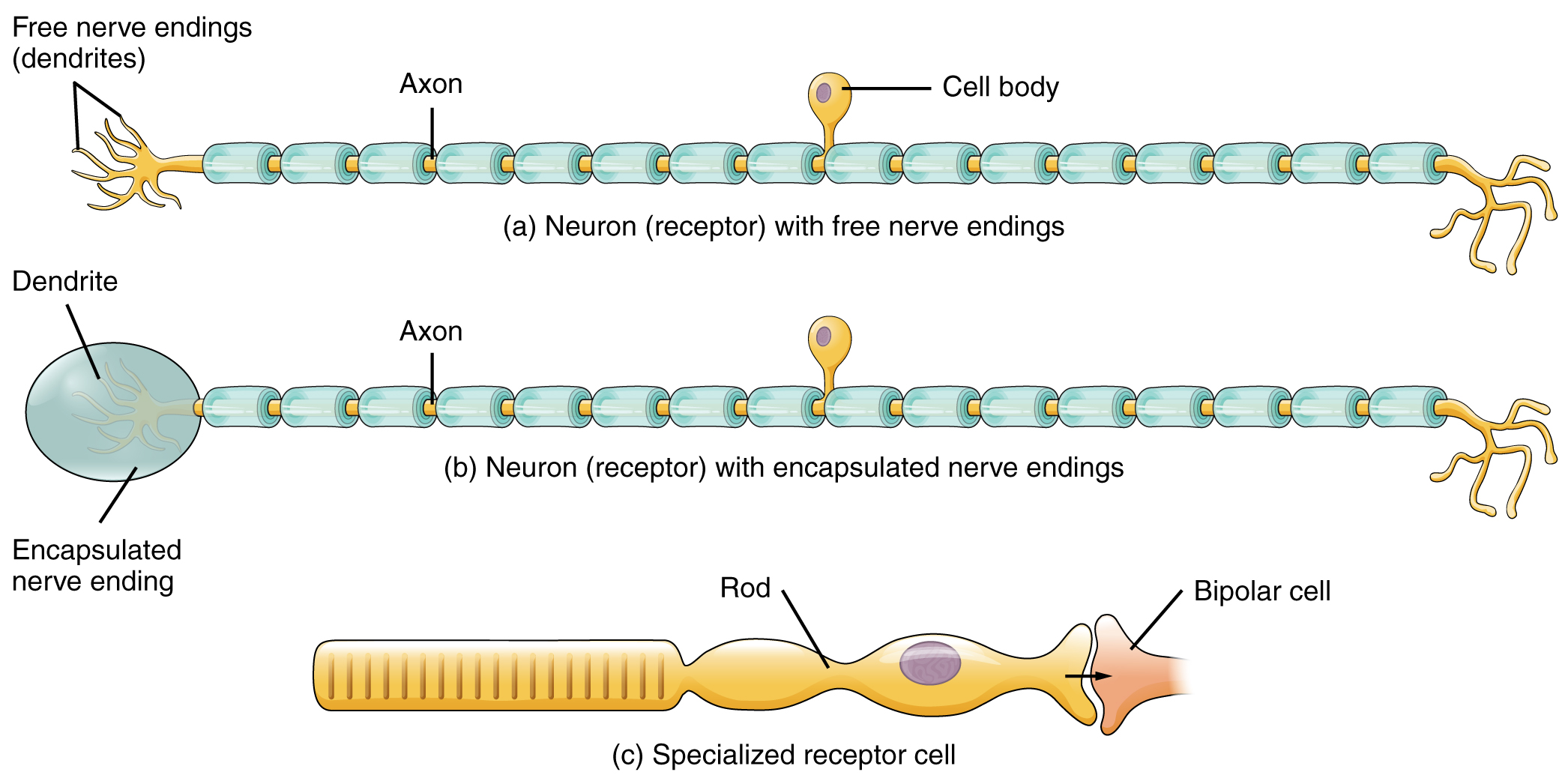
Another way that receptors can be classified is based on their location relative to the stimuli. An exteroceptor is a receptor that is located near a stimulus in the external environment, such as the somatosensory receptors that are located in the skin. An interoceptor is one that interprets stimuli from internal organs and tissues, such as the receptors that sense the increase in blood pressure in the aorta or carotid sinus. Finally, a proprioceptor is a receptor located near a moving part of the body, such as a muscle, that interprets the positions of the tissues as they move.
A third classification of receptors is by how the receptor transduces stimuli into membrane potential changes. Stimuli are of three general types. Some stimuli are ions and macromolecules that affect transmembrane receptor proteins when these chemicals diffuse across the cell membrane. Some stimuli are physical variations in the environment that affect receptor cell membrane potentials. Other stimuli include the electromagnetic radiation from visible light. For humans, the only electromagnetic energy that is perceived by our eyes is visible light. Some other organisms have receptors that humans lack, such as the heat sensors of snakes, the ultraviolet light sensors of bees, or magnetic receptors in migratory birds.
Receptor cells can be further categorized on the basis of the type of stimuli they transduce. Chemical stimuli can be interpreted by a chemoreceptor that interprets chemical stimuli, such as an object’s taste or smell. Osmoreceptors respond to solute concentrations of body fluids. Additionally, pain is primarily a chemical sense that interprets the presence of chemicals from tissue damage, or similar intense stimuli, through a nociceptor . Physical stimuli, such as pressure and vibration, as well as the sensation of sound and body position (balance), are interpreted through a mechanoreceptor . Another physical stimulus that has its own type of receptor is temperature, which is sensed through a thermoreceptor that is either sensitive to temperatures above (heat) or below (cold) normal body temperature.
Ask anyone what the senses are, and they are likely to list the five major senses—taste, smell, touch, hearing, and sight. However, these are not all of the senses. The most obvious omission from this list is balance. Also, what is referred to simply as touch can be further subdivided into pressure, vibration, stretch, and hair-follicle position, on the basis of the type of mechanoreceptors that perceive these touch sensations. Other overlooked senses include temperature perception by thermoreceptors and pain perception by nociceptors.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?