| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Development of the respiratory system begins early in the fetus. It is a complex process that includes many structures, most of which arise from the endoderm. Towards the end of development, the fetus can be observed making breathing movements. Until birth, however, the mother provides all of the oxygen to the fetus as well as removes all of the fetal carbon dioxide via the placenta.
The development of the respiratory system begins at about week 4 of gestation. By week 28, enough alveoli have matured that a baby born prematurely at this time can usually breathe on its own. The respiratory system, however, is not fully developed until early childhood, when a full complement of mature alveoli is present.
Respiratory development in the embryo begins around week 4. Ectodermal tissue from the anterior head region invaginates posteriorly to form olfactory pits, which fuse with endodermal tissue of the developing pharynx. An olfactory pit is one of a pair of structures that will enlarge to become the nasal cavity. At about this same time, the lung bud forms. The lung bud is a dome-shaped structure composed of tissue that bulges from the foregut. The foregut is endoderm just inferior to the pharyngeal pouches. The laryngotracheal bud is a structure that forms from the longitudinal extension of the lung bud as development progresses. The portion of this structure nearest the pharynx becomes the trachea, whereas the distal end becomes more bulbous, forming bronchial buds. A bronchial bud is one of a pair of structures that will eventually become the bronchi and all other lower respiratory structures ( [link] ).
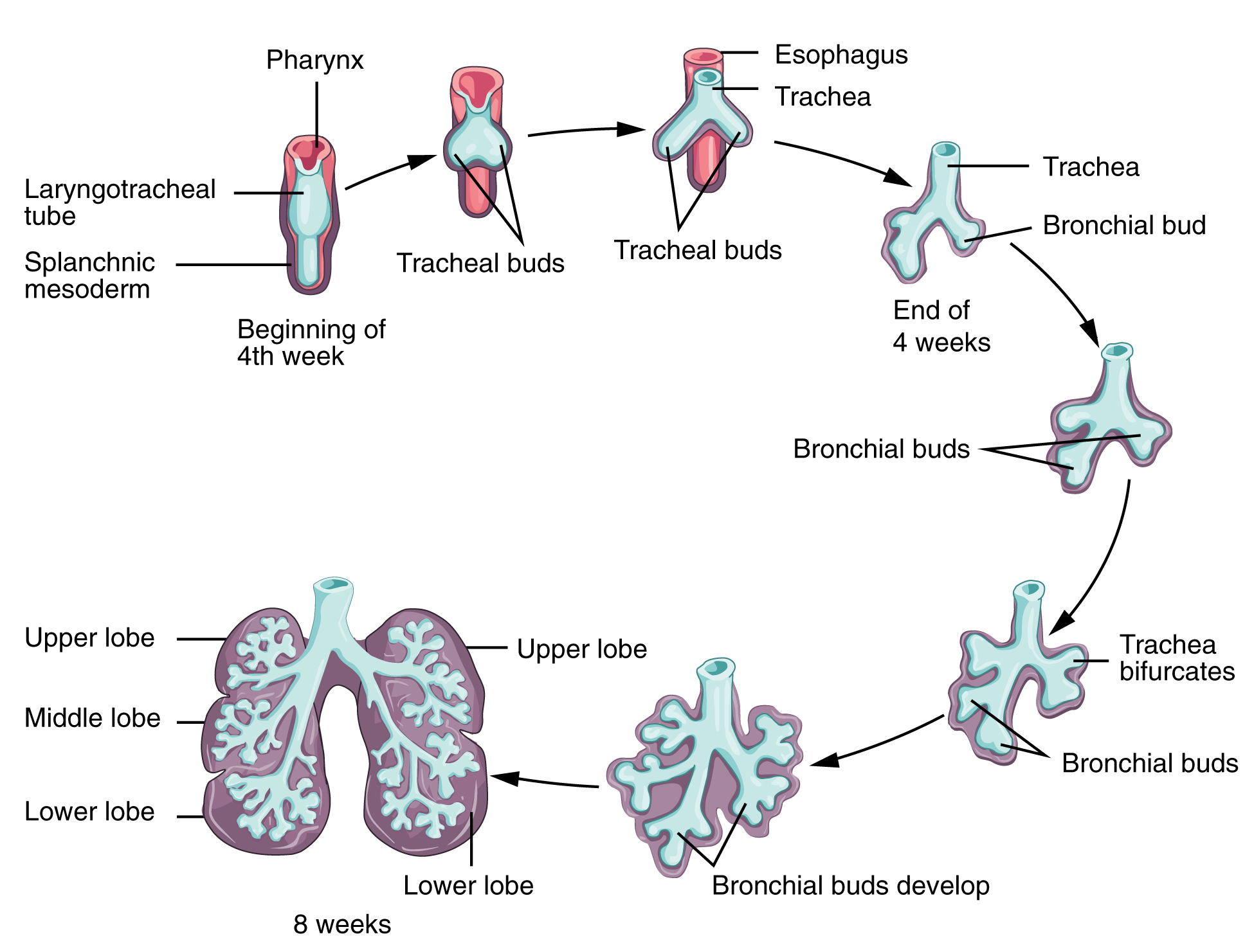
Bronchial buds continue to branch as development progresses until all of the segmental bronchi have been formed. Beginning around week 13, the lumens of the bronchi begin to expand in diameter. By week 16, respiratory bronchioles form. The fetus now has all major lung structures involved in the airway.
Once the respiratory bronchioles form, further development includes extensive vascularization, or the development of the blood vessels, as well as the formation of alveolar ducts and alveolar precursors. At about week 19, the respiratory bronchioles have formed. In addition, cells lining the respiratory structures begin to differentiate to form type I and type II pneumocytes. Once type II cells have differentiated, they begin to secrete small amounts of pulmonary surfactant. Around week 20, fetal breathing movements may begin.
Major growth and maturation of the respiratory system occurs from week 24 until term. More alveolar precursors develop, and larger amounts of pulmonary surfactant are produced. Surfactant levels are not generally adequate to create effective lung compliance until about the eighth month of pregnancy. The respiratory system continues to expand, and the surfaces that will form the respiratory membrane develop further. At this point, pulmonary capillaries have formed and continue to expand, creating a large surface area for gas exchange. The major milestone of respiratory development occurs at around week 28, when sufficient alveolar precursors have matured so that a baby born prematurely at this time can usually breathe on its own. However, alveoli continue to develop and mature into childhood. A full complement of functional alveoli does not appear until around 8 years of age.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?