| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
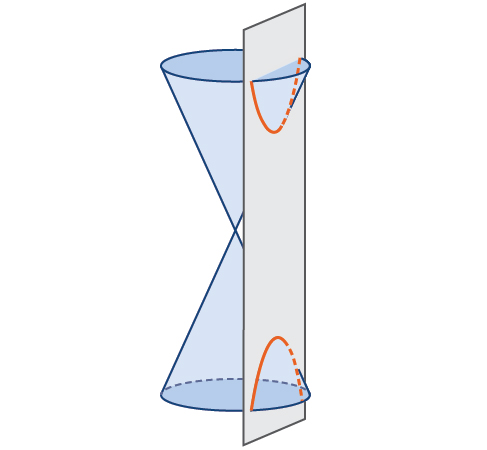
What do paths of comets, supersonic booms, ancient Grecian pillars, and natural draft cooling towers have in common? They can all be modeled by the same type of conic . For instance, when something moves faster than the speed of sound, a shock wave in the form of a cone is created. A portion of a conic is formed when the wave intersects the ground, resulting in a sonic boom. See [link] .

Most people are familiar with the sonic boom created by supersonic aircraft, but humans were breaking the sound barrier long before the first supersonic flight. The crack of a whip occurs because the tip is exceeding the speed of sound. The bullets shot from many firearms also break the sound barrier, although the bang of the gun usually supersedes the sound of the sonic boom.
In analytic geometry, a hyperbola is a conic section formed by intersecting a right circular cone with a plane at an angle such that both halves of the cone are intersected. This intersection produces two separate unbounded curves that are mirror images of each other. See [link] .
Like the ellipse, the hyperbola can also be defined as a set of points in the coordinate plane. A hyperbola is the set of all points in a plane such that the difference of the distances between and the foci is a positive constant.
Notice that the definition of a hyperbola is very similar to that of an ellipse. The distinction is that the hyperbola is defined in terms of the difference of two distances, whereas the ellipse is defined in terms of the sum of two distances.
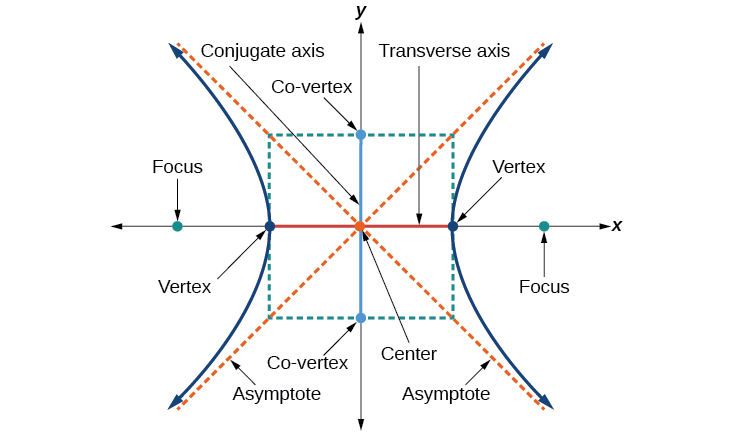
As with the ellipse, every hyperbola has two axes of symmetry . The transverse axis is a line segment that passes through the center of the hyperbola and has vertices as its endpoints. The foci lie on the line that contains the transverse axis. The conjugate axis is perpendicular to the transverse axis and has the co-vertices as its endpoints. The center of a hyperbola is the midpoint of both the transverse and conjugate axes, where they intersect. Every hyperbola also has two asymptotes that pass through its center. As a hyperbola recedes from the center, its branches approach these asymptotes. The central rectangle of the hyperbola is centered at the origin with sides that pass through each vertex and co-vertex; it is a useful tool for graphing the hyperbola and its asymptotes. To sketch the asymptotes of the hyperbola, simply sketch and extend the diagonals of the central rectangle. See [link] .
In this section, we will limit our discussion to hyperbolas that are positioned vertically or horizontally in the coordinate plane; the axes will either lie on or be parallel to the x - and y -axes. We will consider two cases: those that are centered at the origin, and those that are centered at a point other than the origin.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?